I recently had a female patient come in with some concerns related to her menstrual cycle and fibroids. I decided to run a full panel of blood tests and discovered a low vitamin D level but a high calcium level. This is an unusual finding as calcium tends to be normal or low with a low vitamin D level. I immediately sent the patient for a serum Parathyroid Hormone test and it turned out to be elevated. That is what inspired me to write todays blog article.
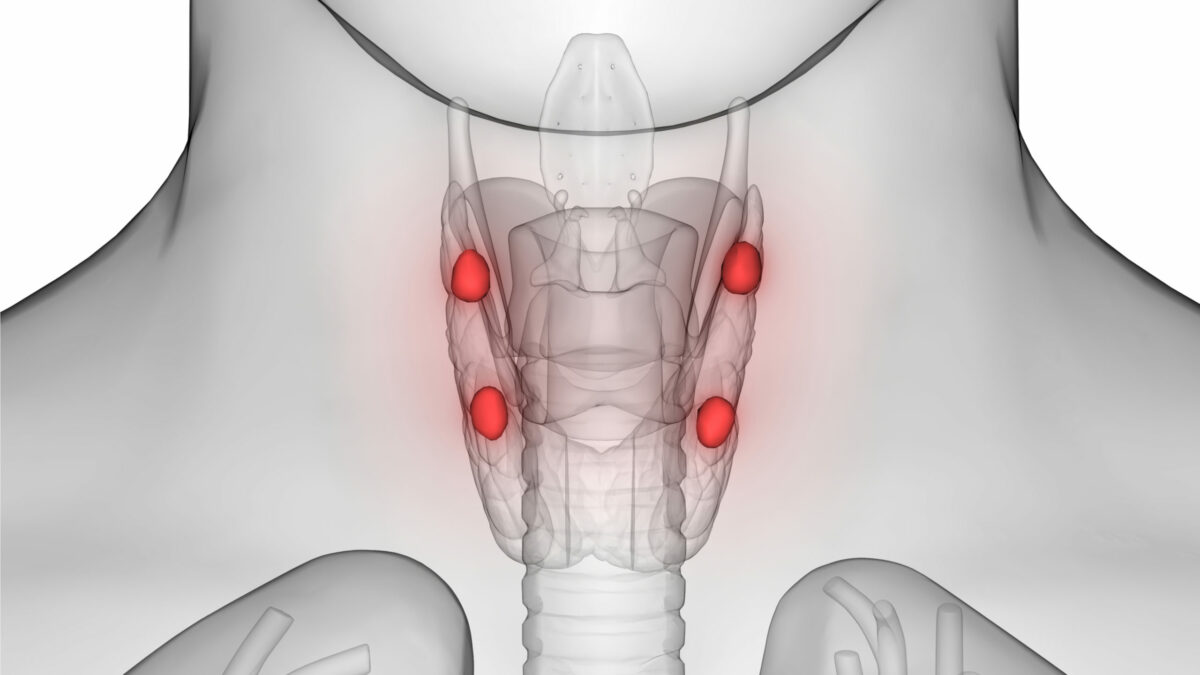
In the intricate orchestra of human physiology, the parathyroid gland is a minuscule yet fundamental player. Despite its small size, this tiny gland, nestled within the larger thyroid, wields significant influence over a critical aspect of human health: calcium regulation. This comprehensive guide aims to cast a bright, educational spotlight on the parathyroid, offering insights into its anatomy, functions, associated disorders, diagnostic methods, and essential roles in maintaining overall health.
Chapter 1: The Parathyroid Gland Unveiled
Understanding Its Anatomy
The parathyroid gland is typically made up of four small, pea-sized nodules located behind the thyroid gland in the neck. These glands, rich in vascular tissue, are integral in the body’s calcium homeostasis, ensuring that levels of this crucial mineral are maintained within the narrow range necessary for normal cell function.
The Vital Role in Calcium Regulation
Calcium is a multi-functional mineral; it’s ubiquitous in the body, integral for nerve conduction, muscle function, blood coagulation, and bone health. The parathyroid hormone (PTH) is the orchestra conductor that maintains the body’s calcium levels, doing so through interactions with the bones, kidneys, and intestines.

Chapter 2: Parathyroid Disorders
Hyperparathyroidism: When Too Much of a Good Thing Goes Awry
Occurring when the parathyroid glands produce too much PTH, hyperparathyroidism can lead to hypercalcemia, a high level of calcium in the blood. This condition can result from a benign tumour on the gland or be a consequence of kidney failure, which impairs calcium excretion.
Hypoparathyroidism: The Paradox of Calcium Insufficiency
Conversely, hypoparathyroidism entails underproduction of PTH, which results in hypocalcemia, or low calcium levels. Autoimmune diseases, injury to the glands during surgery, or genetic disorders can be underlying causes of hypoparathyroidism, leading to symptoms like muscle spasms and mood changes.
Chapter 3: Diagnosis and Treatment
Identifying Parathyroid Disorders
The intricate balance of calcium regulation means that symptoms can be as varied as the diseases themselves. Blood tests to measure PTH and calcium levels, along with imaging studies such as neck ultrasounds, and CT scans, are standard diagnostic tools to elucidate parathyroid issues.
Restoring Balance: Treatment of Parathyroid Disorders
Treatment for parathyroid disorders can range from watchful waiting to managing symptoms with medications. In severe cases, surgical removal of the affected gland, known as a parathyroidectomy, may be the necessary recourse to restore optimal calcium balance.
Chapter 4: The Parathyroid’s Influence on Overall Health
The Bone of Contention: Parathyroid and Skeletal Health
Parathyroid disorders not only discompose the orchestra of calcium balance but have specific ramifications for bone health. Hyperparathyroidism, in particular, can cause weakened bones, a condition known as osteoporosis, affecting an individual’s mobility and overall quality of life.
Building the Big Picture: The Parathyroid’s Interaction with Other Organs
The parathyroid isn’t an island. Its intricate interplay with other organs, particularly the kidneys and the thyroid, further underscores its crucial role in maintaining the complex health harmony within the body. Understanding these interactions sheds light on the far-reaching effects of parathyroid disorders.
Chapter 5: The Future of Parathyroid Research and Health
Advances in Understanding and Treating Parathyroid Disorders
Research and advancements in parathyroid health are crucial as they pave the way for better diagnostic tools and more nuanced treatment options. Genetic studies and the development of targeted therapies are high on the agenda, promising a brighter outlook for those battling parathyroid disorders.
The Power of Prevention and Awareness
Empowerment through knowledge and awareness is the key to preventing and managing parathyroid disorders. Efforts to promote healthy lifestyle choices, regular health screenings, and the dissemination of information on early warning signs can significantly impact the management of parathyroid disorders.
Chapter 6: External Resources and Further Reading
For those interested in further exploration, a wealth of resources is available, including academic journals, medical databases, and reputable health organizations. The complexity and importance of parathyroid health demand continual learning and a collaborative approach among healthcare professionals, patients, and researchers.
In conclusion, the parathyroid gland may be petite, but its position as a regulator of calcium and a pivotal player in human health underscores its colossal importance. Its impact extends beyond its modest physical frame, making it an organ worth acknowledging and understanding in the broader tapestry of the human body.