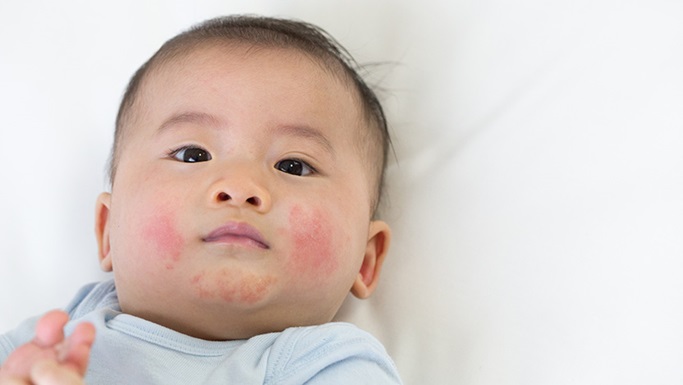
Eczema is a pesky skin condition, and what many don’t realize is that it often comes with a sneaky sidekick: Staphylococcus aureus, a bacteria that can make things a lot worse. For kids with eczema, an overgrowth of staph can lead to some pretty nasty flare-ups, so it’s important to keep it in check. New research shows that probiotics and berberine can help balance the skin’s microbiome and reduce harmful bacteria. By adding these natural remedies to your child’s treatment plan, you can help improve their skin health and reduce the severity of their eczema. Want to learn more about how to help your child? Book an appointment with a Naturopathic Doctor today.
Understanding the eczema-staph connection
Eczema and Staphylococcus aureus are both complex conditions. Understanding them is important to managing this long-term skin condition. Staph aureus, a bacteria we all carry, is often found on the skin of people with eczema. But in those with eczema, it’s more prevalent, and this overabundance can lead to flare-ups and exacerbate symptoms. It disrupts the skin’s natural defences, making it more prone to inflammation and irritation.
Science has our back on this one: studies have consistently linked more severe eczema with higher levels of staph. Armed with this insight, I’ve found that a thoughtful, personalized approach to skin care can help to keep staph at bay and eczema under control.
The common go-to for staph is antibiotics and topical treatments, but they can also throw our skin’s natural balance off-kilter, making things worse. It’s a delicate dance, managing the staph without compromising our skin’s strength. This is where a more comprehensive approach to eczema care comes in, one that takes into account the whole picture, from the bacteria to the environment.
How staph-aureus affects eczema in children
In children, Staphylococcus aureus’ effect on eczema is especially important. It not only makes the skin more inflamed, but it also makes it harder to treat. This bacterium is commonly found on the skin of individuals with eczema, and its presence can exacerbate symptoms, leading to more frequent and severe flare-ups. Children with eczema are especially vulnerable to these effects due to their developing immune systems and the delicate nature of their skin.
Regarding treatment, antibiotics are often the go-to, but they might not be the whole answer. You need to take care of your skin, too. That means sticking to a regular skin care routine, using gentle soaps, and making sure your skin is well-moisturized. Some research has suggested that probiotics might be able to help, too. By keeping your skin’s microbiome in balance, probiotics can help your skin fight off staph and keep it from getting out of control.
And then there’s berberine, a little gem found in certain herbs. It’s like a superhero that can put a stop to the staph’s mischief, making it a great sidekick to traditional treatments. When you use these natural wonders in your child’s eczema care, you’re not just treating the symptoms—you’re building a foundation for long-term skin health. It’s a comprehensive strategy, and it’s all about giving your child the very best.

Probiotics: A promising defence against staph
Probiotics, often linked to gut health, are now being recognized for their ability to fight staph infections. They offer a natural way to help the skin’s microbiome. Probiotics can help balance the skin’s ecosystem, just like they do for our digestive system. They can also reduce the presence of harmful bacteria like Staphylococcus aureus. This equilibrium is especially vital for those with eczema, as an unbalanced microbiome can trigger symptoms and flare-ups.
It’s fascinating—research has unveiled that probiotics can be a game-changer for kids with eczema. There’s a study published in the Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology, that discovered how children who took probiotic supplements saw a real drop in the severity of their eczema. And then there are topical probiotics that are getting a lot of buzz for how they can form a protective shield on the skin. They’re like knights in shining armour, warding off bad bacteria, especially Staphylococcus aureus. By teaming up with these friendly bacteria, the skin is better equipped to fight off infections and heal, which is a huge relief for kids dealing with eczema.
Probiotics are great on their own, but when you add other natural remedies like berberine, they are even stronger. Berberine, a little something found in certain herbs, is like a secret agent—it’s got antimicrobial properties that can really take on Staphylococcus aureus. So, by bringing probiotics and berberine together, we’re talking about a tag team that’s got eczema on the ropes. Talking to a Naturopathic Doctor can make sure these natural heroes are working safely and well, especially for our children.

Berberine: An herbal approach to managing eczema
Berberine, a herb with a rich history of antimicrobial use, is now in the spotlight as a natural ally in the fight against eczema and the bacteria Staphylococcus aureus. This ancient remedy, with roots in traditional medicine, is gaining modern recognition for its potential to support skin health. Its anti-inflammatory properties are especially good for people with eczema. It may help reduce the redness, itching, and discomfort that often happen when their skin gets worse.
But Berberine doesn’t stop there. It’s like a guardian for your skin’s defences, helping to fortify its natural barriers. This is especially important for young people with eczema. Their skin is often more sensitive and can let in unwanted guests like the Staph aureus bacteria, which can make eczema symptoms worse. By shoring up these defences, berberine can help create a healthier, more resilient skin environment.
Studies have revealed that berberine’s antimicrobial prowess is a powerful ally in the fight against Staph bacteria. It’s a great natural treatment for eczema. When used with traditional treatments, it gives you a complete skin care plan. By weaving berberine into our daily skin rituals, we’re not only boosting the effectiveness of our current routines but also nurturing our skin from within. It’s a beautiful blend of nature and science, and it’s a gift we can give our little ones—a more complete way to care for their eczema.
Integrating natural solutions with medical treatment
Integrating natural solutions like probiotics and berberine with conventional medical treatments can provide a comprehensive approach to managing eczema and improving quality of life. For many children, using these natural remedies with traditional treatments like topical steroids can lead to better and longer-lasting results. Topical steroids are a cornerstone of eczema treatment, helping to reduce inflammation and soothe irritated skin. However, adding probiotics can make these treatments even more effective by helping the skin protect itself and promoting a healthy microbiome.
But here’s the thing: while it’s pretty clear that combining natural and medical treatments can be a game-changer, it’s super important to do this the right way, with a healthcare professional by your side. A naturopath can be a guiding light, offering personalized recommendations to make sure those natural solutions are both safe and effective. They’ll help keep an eye on how your child is responding to the combined treatments and make any tweaks to the plan as needed. Working with a naturopath, parents can feel good about the well-rounded and holistic approach they’re taking to help their child manage eczema.
Adding natural remedies like probiotics and berberine to an eczema care plan can be a big help for your child’s skin and overall health. It’s about weaving together the best of both worlds—traditional and natural—to help your child feel more at home in their skin and in their life.