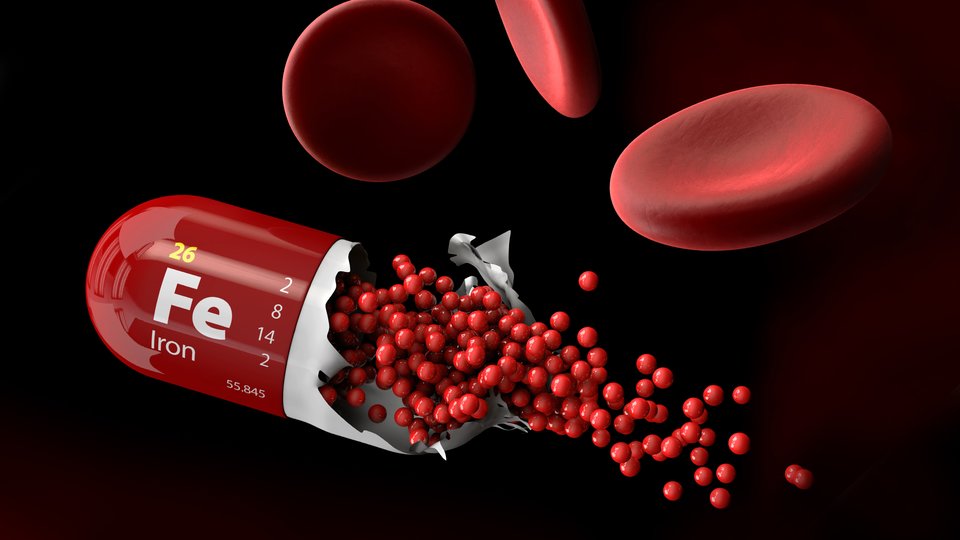
Iron is a fundamental nutrient that our bodies can’t live without. It plays an instrumental role in the formation of hemoglobin, a protein in red blood cells that transports life-sustaining oxygen to every corner of our body. However, a deficiency of this vital mineral can lead to anemia, a condition marked by a lack of healthy red blood cells or hemoglobin in the body. This can result in a host of health problems, including fatigue, weakness, and even severe health complications.
Fortunately, iron supplements are a readily available solution that can help prevent and treat iron-deficiency anemia. With countless iron supplements on the market, it can be difficult to discern which one is best for you. In this article, we delve into the different types of iron supplements, their chemical compositions, and the specific studies that have used them to treat iron-deficiency anemia.

Ferrous Sulfate:
As the most common and cost-effective type of iron supplement, ferrous sulfate is a go-to solution for many. Available in both tablet and liquid form, it is easily accessible over the counter. Its chemical composition allows for optimal absorption when taken on an empty stomach. However, its usage can lead to side effects like constipation, nausea, and stomach upset. Despite these potential drawbacks, ferrous sulfate is often the first line of defense against iron-deficiency anemia and is a suitable supplement for those with low iron levels. A study published in the British Journal of Nutrition found that ferrous sulfate was effective in improving iron status in anemic women.
Ferrous Fumarate:
Ferrous fumarate distinguishes itself with its superior absorption compared to ferrous sulfate. This means it can deliver significant results in a shorter timeframe. Although available over the counter, it’s typically prescribed to patients with severe iron-deficiency anemia. Side effects such as constipation and stomach upset can still occur but are usually well-tolerated. A 2014 study published in PLOS ONE concluded that ferrous fumarate had a similar efficacy and tolerability to other iron preparations.
Iron Glycinate:
Known for its high bioavailability, iron glycinate is a type of iron supplement that is absorbed more easily by the body when compared to other types. This makes it an attractive option for individuals with low iron levels seeking an effective supplement with minimal side effects. Its chemical composition also makes it gentler on the stomach, making it a preferred choice for many. A 2017 study in the Journal of International Medical Research found iron glycinate to be a safe and effective treatment option for iron-deficiency anemia.
Iron Bisglycinate:
Iron bisglycinate is a gentle-on-the-stomach supplement that can be taken on an empty stomach. It is readily absorbed by the body, providing rapid results for those with low iron levels. However, it’s typically more expensive than other iron supplements. It’s an excellent choice for individuals who have experienced stomach-related side effects from other iron supplements. A study published in Nutrition Research found that iron bisglycinate was as effective as ferrous sulfate in treating iron-deficiency anemia, with fewer gastrointestinal side effects.
Heme Polypeptide Iron:
Heme polypeptide iron is a unique supplement derived from animal sources. Chemically similar to the iron found in hemoglobin, it is easily absorbed by the body and can be especially effective for individuals with iron-deficiency anemia or conditions that hinder iron absorption. Its primary advantage over other iron supplements is its reduced likelihood of causing gastrointestinal side effects like constipation, nausea, and stomach upset. Unlike many other iron supplements, heme polypeptide iron can be taken with or without food. However, due to its animal origin, it may not be suitable for vegetarians or vegans, and it’s generally more expensive. A study in the American Journal of Clinical Nutrition found that heme iron polypeptide provided a well-tolerated and effective option for the treatment of iron-deficiency anemia.
For more about iron deficiency anemia Click Here
Conclusion:
In conclusion, iron is a crucial element for our body’s overall health and wellbeing. Its deficiency can lead to anemia, posing serious health risks. Thankfully, there are various iron supplements available to prevent and treat this condition. Whether it’s the commonly used ferrous sulfate, the easily absorbed ferrous fumarate, the gentle-on-the-stomach iron glycinate, the quick-acting iron bisglycinate, or the animal-based heme polypeptide iron, each has its unique benefits and potential drawbacks. The choice of supplement largely depends on individual needs, tolerance, and lifestyle. It’s essential to remember that while supplements can help restore iron levels, they should not replace a balanced diet rich in iron. Always consult with a healthcare professional before starting any new supplement regimen. Your health is your wealth, so take the necessary steps to ensure it’s well-managed.