THC and CBD the ABC’s of Medical Marijuana
The perspective of a Naturopathic Doctor
As a practicing Naturopathic Doctor, I have understandably been occupying a front row seat in what has become one of today’s hot topic health issues; the use of medical marijuana. I have seen a trend recently in my patients; they’re dropping the conventional pain medications and experimenting with the unquestionably still taboo, cannabis. Two things seem to be driving this phenomenon: traditional pain medications aren’t doing the trick anymore and there is a curiosity about this promising although misunderstood plant.
Professionally, I too have been very curious about the medical applications of marijuana. For years patients would confide in me and share their experiences with using different preparations of cannabis. One of the usual preparations is “hemp oil”, which can contain a significant amount of a cannabinoid called CBD. Hemp oil may have been dismissed as folk remedy; however, with the recent surge in medical marijuana use prompting an educated examination of a potential effective therapy. I can now appreciate that hemp oil is a way to reap the benefits of cannabis without getting intoxicated.
There are thousands of articles on the web that explain in depth what the different components of marijuana are and how they differ in pharmacology and therapeutic applications. The point of this article is not to give a thesis but rather present a concise easy to grasp understanding of what those components do in the body and why cannabis in one form or another should be considered as a first choice medicine.
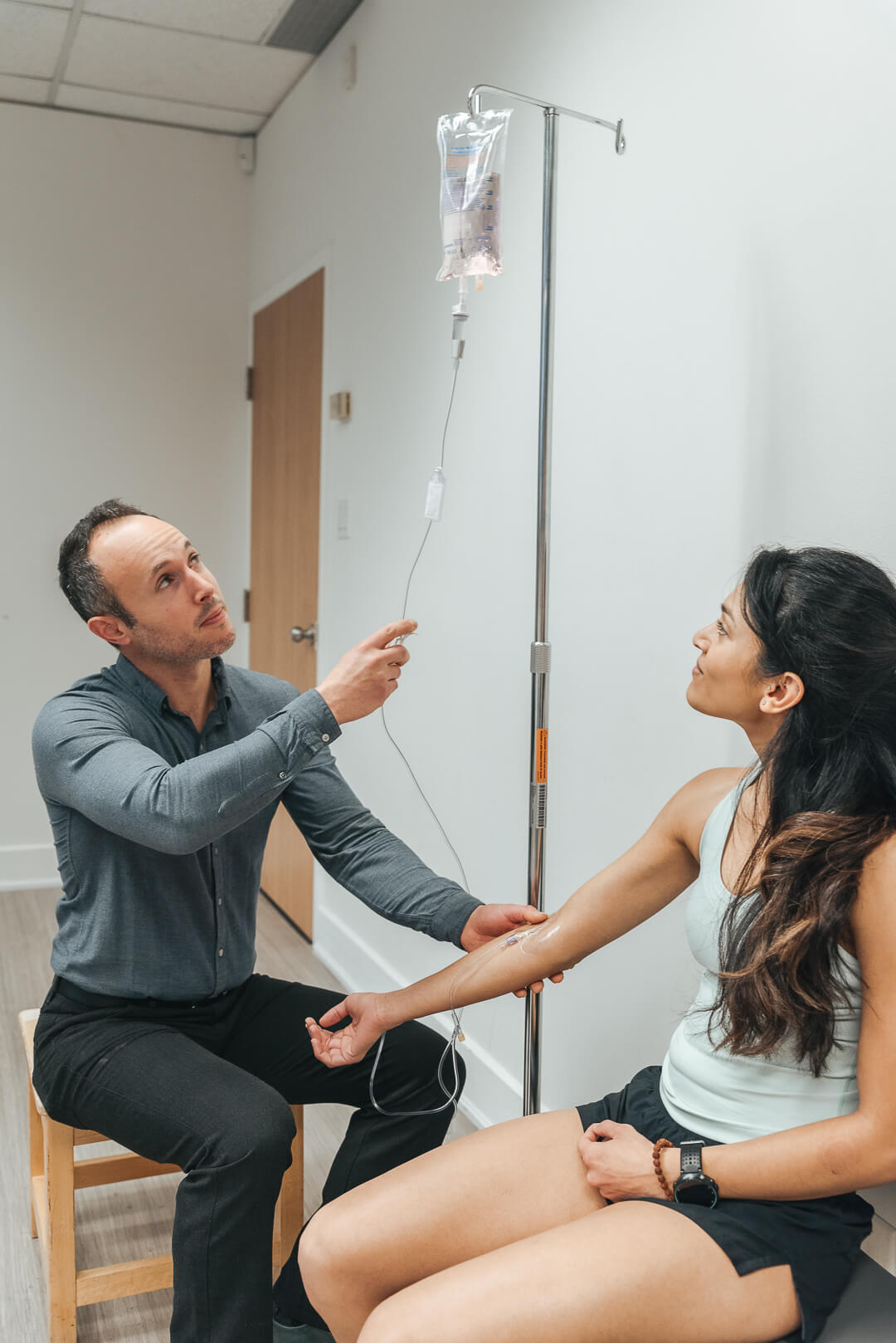
Before presenting the different types and components of marijuana, I would like to give this article some context and legitimacy by introducing myself, and my medical background. I am a Naturopathic Doctor and have been in private practice for just over 7 years in Toronto Canada. Over the past 4 years my practice has focused on the treatment of pain, debilitating neurological conditions and cancer. This really sets the stage as the first few regulated cannabis medications in Canada, namely Nabilone and Sativex, were approved for neuropathic pain, spasticity and nausea associated with cancer treatment and multiple sclerosis; both of which I see more consistently than the average naturopathic doctor. Naturally I started having patients that had experience with these medications or who were experimenting with unregulated forms of cannabis.
A watershed moment in my practice occurred when I began treating a 10-year-old girl that had suffered a stroke. I thought she would benefit from cannabis but at the same time was hesitant about subjecting her to the hallucinogenic properties of THC. Fortuitously around that very same time I viewed a CNN Sanjay Gupta report about a low THC / high CBD strain of marijuana called “charlottes web”. Treatment with this strain had been helping a young girl with a rare debilitating condition associated with frequent seizures. My young patient didn’t have seizures but had chronic high muscle tone as is also seen during seizures. The report also mentioned how CBD is not hallucinogenic. I was certainly intrigued as to the potential efficacy of this treatment and devoted both time and resources in understanding medical cannabis and CBD. As a result of this study and promising results, I now recommend CBD regularly in my practice. Now let’s take a step back and understand what CBD is and what does it do.
Although there are thousands of potentially therapeutic compounds in cannabis, research has really focused on two: THC and CBD. Depending on the sex and strain of the cannabis some will be higher or lower in one compound than the other.
THC is what gets you high. It acts on cannabinoid receptors in the body and brain with the result of inducing the perception altering experience that marijuana is known for. Along with the “high”, research has pointed out that there are definite pain lowering and mood enhancing properties of THC. However; there are some concerns with THC as it may impact learning in the developing brain, may trigger a psychotic episode in individuals predisposed to schizophrenia and impacts the users ability to carry out daily living tasks such as operating machinery and driving.
CBD, on the other hand, is a non-psychoactive component of cannabis that can comprise up to 40% of the active cannabinoids in marijuana. Although large doses of CBD in my experience can induce an intense feeling of relaxation there are no perception altering effects from even the highest doses of CBD. Research into this curious compound has pointed out that rather than binding to cannabinoid receptors in the body, as does THC, CBD for the most part blocks activity at these receptors and exerts most of its effect at a receptor called 5-HT1a. The 5-HT1a-receptor is linked to serotonin activity.
The overall effect of CBD in the complicated milieu of the human body is that it is anti-inflammatory, mood enhancing, offers protection for the nervous system, promotes relaxation, anti-spasmodic and negates some of the unwanted side-effects of THC consumption. CBD has even been shown to prolong the beneficial effects of THC by increasing the body’s amount of cannabinoid receptors. Furthermore, there has yet to be any evidence for negative side effects or toxicity even at very high doses of CBD per day. CBD research is currently exploring promising therapeutic effect in epilepsy, dementia, migraine and cancer. So all in all it’s a pretty impressive compound.
Now you may be wondering; “how do I get CBD?” – do I need a prescription and is it legal? Technically in Canada any derivative of Marijuana including THC and CBD is classified as a schedule 2-drug and can only be legally obtained with a prescription from a medical doctor. Personally I find it frustrating that Naturopathic Doctors, who receive 4 years of training in botanical medicine, are restricted from prescribing marijuana (a botanical last time I checked) whereas the responsibility falls on medical doctors who typically have no training in prescribing botanical preparations. Fortunately hemp, which is part of the cannabis family, is high in CBD, low in THC and in some cases legal (The legality of the extraction depends on factors such as THC levels and what part of the plant is used).
There are now many companies which specialize in CBD preparations derived from hemp and do not require a prescription from a medical doctor. Unfortunately the CBD on the market continues to be a bit pricey per milligram ($1/10mg) since a therapeutic dose often starts at around 40mg all the way up to 200mg per day. Hopefully in the future we will start to see some higher potency, cheaper preparations of CBD.
As a Naturopathic Doctor, I offer the following personal and professional perspective to both botanical medicines as a whole and specifically CBD. Medicines derived from whole botanicals are a complex collection of thousands of compounds. Often we really only have an understanding of a few of those compounds and that is what disorients many practitioners, especially medical doctors. However, I believe we should appreciate the complexity of botanical medicines precisely because our own physiology is just as complex. Pharmaceutical preparations are very specific in their composition and action in the body. Our bodies are not built that way and that is why we often see side effects with pharmaceutical preparations.
Certainly I do not claim that there are no side effects with botanical medicines, but it is a fact that there are far fewer. Pharmaceutical medicines have a definite time and place in specific treatment but we should not be frightened to use botanical medicines because it is their complexity that often make them safer for prolonged use proving for a more balanced therapeutic effect.
During my relatively short period of recommending CBD, I have seen the benefits in: Pain, Sleep, Focus and Rigidity. I work with a great deal of patients who have suffered from neurological injuries (Spinal cord injury, brain injury, stroke) and neurological disease (Multiple Sclerosis, Transverse Myelitis, Chronic Regional Pain Syndrome, Migraine, Fibromyalgia). I have witnessed more than half of these clients taper down or completely come off of several pain medications including addictive opioid medications and manage their symptoms more effectively with a combination of THC and CBD.
I have a number of patients who after several years of insomnia return to a normal sleep pattern with a therapeutic program that includes CBD. Many of my clients with high tone and muscle rigidity experience a relaxation response within minutes of taking CBD. In fact patients will often take a dose of CBD during a treatment session and will see the effects immediately. I have several patients tell me that since starting CBD their thinking has been clearer. I even have one patient who has told me that her vision is clearer, which makes sense in the context of inflammation of the optic nerve often experienced in multiple sclerosis.
As a Naturopathic Doctor it is my job to be on top of the latest research and treatment-options within the realm of nutraceuticals, complimentary therapies and herbal medicines. CBD is an exciting new treatment option with an excellent safety profile, promising results and that fits in well with my patient population. I am proud to an advocate for medical marijuana and have made a commitment to continue to update my patients and peers as to my clinical experience with CBD.