Type 2 diabetes is a serious and growing health concern, with over 29 million Americans affected by the disease. Eating apples has been linked with a lower risk of type 2 diabetes. This is likely due to the fact that apples contain pectin. Pectin helps to slow the digestion and absorption of carbohydrates, which helps to keep blood sugar levels stable. Additionally, apples are a good source of antioxidants, which can help improve insulin sensitivity.
Because they’re high in fiber and water, apples can help you feel fuller longer and prevent overeating throughout the day.
Multiple sclerosis is a debilitating neurological disorder that can often leave patients feeling hopeless and alone. But there is hope! In this blog post, we will explore nine natural treatments for multiple sclerosis that have helped my Toronto patients alleviate some of the symptoms associated with the disease.
1. Acupuncture
Acupuncture is a traditional Chinese medicine technique that involves inserting thin needles into the skin at specific points on the body. It is believed that this helps to clear energy blockages and promote balance and healing within the body. There is some evidence to suggest that acupuncture may be effective in treating symptoms of multiple sclerosis, such as fatigue, pain, spasticity, and bladder problems.
2. Herbal Medicine
There are many different herbs that have been traditionally used to treat various ailments, including multiple sclerosis. Some of the most common herbs used for MS include ginger, ginkgo biloba, turmeric, milk thistle, lions mane and green tea. These herbs can be taken in pill form or brewed into a tea. It is important to talk to a Naturopathic Doctor or qualified herbal practitioner before starting any herbal treatment regimen, as some herbs can interact with medications you may be taking for your MS.
3. Dietary Changes
Making some simple dietary changes can also help improve symptoms of MS. One study showed that following a Mediterranean diet—which includes lots of fresh fruits and vegetables, whole grains, fish, and olive oil—may help reduce inflammation and slow the progression of MS. Other helpful dietary changes include avoiding processed foods and food allergies, getting enough vitamin D, and drinking plenty of water.
Food sensitivity testing can help to identify gluten sensitivity and other food sensitivities in people with MS and other autoimmune diseases. The most common type of food sensitivity test is an Elimination Diet, in which potential triggering foods are eliminated from the diet for a period of time and then reintroduced one at a time to see if symptoms occur. However, Elimination Diets can be difficult to stick to and can take months or even years to complete. Another option is an IgG Food Sensitivity Test, which measures levels of immunoglobulin G (IgG) antibodies in the blood.
Antibodies are produced by the immune system in response to perceived threats, such as bacteria or viruses. However, in people with food sensitivities, the immune system overreacts to harmless proteins found in certain foods, producing excessive amounts of IgG antibodies. IgG Food Sensitivity Tests can be helpful in identifying food sensitivities because they can measure levels of IgG antibodies specific to each individual food protein. This allows for a more targeted Elimination Diet and can speed up the diagnosis process. If you think you might have a food sensitivity, you can book an appointment for testing.
4. Exercise
Exercise is important for everyone, but it is especially crucial for those with MS. Regular physical activity can help reduce fatigue, improve mobility and coordination, ease depression and anxiety, promote better sleep, and boost overall fitness and well-being. Even if you are not able to do strenuous exercise due to your symptoms, there are still many low-impact activities you can do to get moving and feeling better.
5. Stress Reduction Techniques
Stress is a well-known trigger for multiple sclerosis (MS) flare-ups. Managing stress is therefore an important part of MS treatment. Stress management techniques such as relaxation therapy and yoga can be helpful, but some patients may also benefit from taking adaptogens. Adaptogens are a class of natural substances that help the body to adapt to stress by reducing the production of stress hormones. They have been used for centuries in traditional Chinese and Indian medicine, and are now gaining popularity as a natural treatment for stress and anxiety. Some common adaptogens include ashwagandha, holy basil, and ginseng. If you are interested in trying adaptogens, talk to your Naturopathic doctor first to discuss whether they are right for you.
6. Vitamin D
Vitamin D is an important nutrient that helps the body absorb calcium. It’s found naturally in very few foods, so most people get it from exposure to sunlight. Vitamin D is also available in supplement form. Some studies suggest that vitamin D may play a role in helping to prevent or treat MS. If you think you might be deficient in vitamin D, book an appointment with us for vitamin D testing or talk to your doctor.
Sometimes supplementation is ineffective or can take too long to bring up severely deficient vitamin D levels. I offer these patients the option of a high potency vitamin D injection that will bring levels up very quickly.
7. Mitochondrial Support
Mitochondrial support using resveratrol, alpha lipoic acid, coenzyme Q10 and NAD boosters is a promising new treatment for patients with multiple sclerosis. Mitochondria are the powerhouses of the cell, and they are responsible for producing energy. In patients with multiple sclerosis, the mitochondria are not working properly, and this can lead to fatigue and other symptoms. Resveratrol, alpha lipoic acid, coenzyme Q10 and NAD boosters help to support the mitochondria and improve their function. In a small study of patients with multiple sclerosis, those who received mitochondrial support had less fatigue and improved quality of life.
8. Hormones
Hormones play an important role in the human body, regulating everything from metabolism and mood to reproduction and energy levels. When hormones are out of balance, it can lead to a host of problems. For patients with multiple sclerosis (MS), hormone imbalances can cause fatigue, weight gain, depression, and loss of libido. Hormone testing can help to identify imbalances and allow for tailored treatment plans that use bio identical hormone replacement therapy to restore balance. By addressing hormone imbalances, patients with MS can improve their quality of life and potentially reduce their risk of disease progression.
9. Cannabinoids
Recently, cannabinoids have emerged as a potential therapy for MS. Cannabinoids are compounds found in the cannabis plant, and they have been shown to have anti-inflammatory and neuroprotective effects. In animal studies, cannabinoids have been shown to reduce inflammation and nerve damage in models of MS. In small clinical trials, cannabinoids have been shown to improve symptom control in patients with MS. These promising results have led to the development of several cannabinoid-based medications for MS. Dr. Shawn Meirovici N.D. is experienced cannabis educator in Toronto, Ontario. Dr. Shawn can help patients decide if cannabis therapy would be a good addition to their treatment plan.
Conclusion:
If you are living with multiple sclerosis (MS), know that you are not alone—there are millions of other people around the world dealing with this disease every day. And while there is no cure for MS at this time, there are many different treatments that can help alleviate some of the symptoms associated with the disease. In this blog post, we explored nine natural treatments for MS—acupuncture , herbal medicine , dietary changes , exercise , stress reduction techniques, vitamin D, mitochondrial support, hormone balancing and cannabinoid therapy. Make an appointment with us or talk to your doctor about which treatments might be right for you.
What is a healthy lunch for school kids?
You want your kids to have a healthy lunch, but you’re not sure what that looks like. You know they need protein, carbs, phytonutrients and fibre, but how much of each? And what are some good sources of each? Here’s a quick rundown of what a healthy lunch for school kids looks like.
Protein
Kid’s need about 5-6 ounces of protein per day. As a parent, it can be difficult to ensure that your child is getting enough protein in their diet. The good news is that there are plenty of great sources of protein available, including lean meats, tofu, beans, lentils, nuts and seeds.
However, one challenge parents may face is finding ways to work around common nut and seed allergies. If your child or a classmate is allergic to nuts or seeds, be sure to check with your naturopath or pediatrician for suggestions on alternate sources of protein. There are plenty of good options available, including lean meats, tofu, beans, lentils and plant-based protein powders.
Carbs
Carbs are the body’s main source of energy. Kids need about 3-5 ounces of carbs per day. Complex carbs are the body’s main source of energy. They are made up of long chains of sugar molecules that the body can slowly break down and use for energy. Simple carbs are made up of short chains of sugar molecules and the body can break them down quickly for energy. Good sources of complex carbs include fruits, vegetables and whole grains. Some examples of complex carbs that kids would enjoy include:
-Oatmeal
-Quinoa
-Brown rice
-Sweet potatoes
-Fruits like apples, bananas and berries
-Vegetables like broccoli, cauliflower and carrots
Phytonutrients
Phytonutrients are important for kids because they help protect against disease and promote good health. Phytonutrients include antioxidants, which are important for helping to protect the body from damage caused by harmful molecules called free radicals. Free radicals can damage cells, leading to diseases such as cancer. Antioxidants help to counteract the effects of free radicals, preventing or slowing down cell damage. Some good sources of phytonutrients for kids include fruits, vegetables, herbs and spices. Some examples of antioxidant rich foods that kids would enjoy include blueberries, raspberries, strawberries, blackberries, cherries, tomatoes, bell peppers, broccoli, kale and spinach. These foods are packed with nutrients that are good for kids’ growing bodies.
Fibre
Fibre is an important part of a healthy diet. It helps the body feel full and can help with weight loss and maintenance. Kids need about 25 grams of fibre per day. Fibre comes in two forms: soluble and insoluble. Soluble fibre dissolves in water and can help lower cholesterol and blood sugar levels. Good sources of soluble fibre include oats, legumes, apples and berries. Insoluble fibre does not dissolve in water and helps with bowel regularity. Good sources of insoluble fibre include whole grains, vegetables and fruits with skins.
Conclusion
A healthy lunch for school kids should include a variety of protein, carbohydrate and fiber-rich foods to ensure that they are getting the nutrients they need to stay energized and focused throughout the day. While nuts and seeds are healthy sources of protein, fat and fiber, there are other healthy alternatives for those whose schools do not allow them. Parents should always consult with their pediatric naturopath, pediatrician or dietician to create a healthy lunch plan that meets their child’s specific needs.
What can I do beyond steroids?
If your child has eczema, you are not alone. Eczema is a common skin condition affects about 10 to 20 percent of infants and about 3 percent of adults and children. While there is no cure, eczema can be managed with medical treatments and home care. The goal is to reduce inflammation and itchiness, and to prevent new flare-ups. When using steroidal creams for treatment, many parents wonder if there are natural ways to soothe their child’s eczema flare-ups?
The good news is that there are! When used alone or together with steroids, these natural treatments can help manage your child’s eczema flare-ups:
Food Sensitivity Testing
With eczema, the skin is a reflection of what’s going on inside the body – specifically in the gut. A food sensitivity test can help assess intestinal permeability (leaky gut) and inflammation. Once problem foods are identified, they can be eliminated from the diet, which can help reduce inflammation and improve gut health.
Probiotics
Probiotic strains may help balance the immune system and reduce inflammation. Probiotics can be taken orally in the form of supplements or food (such as yogurt).
Omega 3 Fatty Acids
These healthy fats promote a healthy lipid bilayer, which helps keep skin hydrated and supple. Omega 3 fatty acids can be taken orally in supplement form or applied topically as part of a natural eczema cream.
Vitamin D3
Vitamin D3 is a natural anti-inflammatory vitamin that helps boost the immune system. It can be taken orally in supplement form or applied topically as part of a natural eczema cream.
Zinc
Zinc is an essential mineral that plays a role in immune function and tissue repair. It can be taken orally in supplement form or applied topically as part of a natural eczema cream.
Conclusion
While there is no cure for eczema, it can be managed with medical treatments and home care. When used alone or together with steroids, these natural treatments can help soothe your child’s eczema flare-ups: food sensitivity testing, probiotics, omega 3 fatty acids, vitamin D3, zinc.
Book an appointment today!
Do you feel like you’re always getting sick? Are you constantly battling colds and the flu? If so, you may need to boost your immunity. Luckily, there are a number of natural treatments that can help. In this blog post, we will discuss some of the best ways to improve your immune system naturally.
Vitamin D for immunity
Vitamin D is essential for a strong immune system. It helps the body to produce antibodies, which fight infection. Vitamin D can be found in fatty fish, eggs, and fortified milk. You can also get Vitamin D from exposure to sunlight.
Trouble keeping up with vitamin D supplements and worried about sun exposure? Not to worry, at my clinic we offer the option of a vitamin D injection. Under professional supervision, this is a safe and effective way to boost vitamin D levels quickly.
Vitamin C for immunity
Another important nutrient for immunity is Vitamin C. Vitamin C helps the body to create white blood cells, which fight infection. Vitamin C can be found in citrus fruits, tomatoes, bell peppers, and broccoli.
Intravenous vitamin C is a great way to get a high dose of Vitamin C. By bypassing digestion, IV vitamin C can boost levels quickly. Intravenous vitamin C can also increase blood concentrations at levels that directly kill pathogens and inhibit cancer growth.
Zinc for immunity
Zinc is another important mineral for immunity. It helps the body to create new cells and enzymes that fight infection. Zinc can be found in oysters, beef, pork, chicken, and beans.
Zinc can also be added to intravenous infusions for an added immune system boost.
Elderberry Syrup
If you’re looking for a kid friendly and great tasting way to boost your immunity, elderberry syrup is a great option. Elderberries are rich in Vitamin C, Vitamin A, and antioxidants. They have been shown to reduce inflammation and fight infection. You can find elderberry syrup at most health food stores.
Ginger for immunity
Ginger is another great option for boosting your immunity. Ginger is a natural anti-inflammatory and can help to reduce congestion. It can also help to soothe a sore throat. You can find ginger in the form of capsules, tea, or syrup.
Garlic for immunity
Garlic is another excellent food for boosting your immunity. Garlic is rich in Vitamin C, sulfur, and antioxidants. It has been shown to fight infection and reduce inflammation. You can add garlic to your food or take it in supplement form.
Selenium for immunity
Selenium is a trace mineral that is important for immunity. Selenium helps the body to produce antibodies, which fight infection. It can be found in Brazil nuts, tuna, shrimp, and eggs.
Selenium can also be added to an intravenous infusion for an added immune boost.
Vitamin A for immunity
Vitamin A is an important nutrient for immunity. Vitamin A helps the body to produce white blood cells, which fight infection. Vitamin A can be found in sweet potatoes, carrots, dark leafy greens, and squash.
Probiotics for immunity
Probiotics are live bacteria that are good for your gut health. Probiotics help to keep the balance of good and bad bacteria in your gut. This can help to improve digestion and boost immunity. You can find probiotics in yogurt, kimchi, sauerkraut, and kombucha.Probiotic supplements are also available.
There you have it! These are just a few of the best ways to boost your immunity naturally. By including these foods and supplements in your diet, you can help to keep yourself healthy and avoid getting sick. In individuals requiring an extra boost, injection and intravenous treatments are available and effective. Do you have any other favourite natural immunity boosters? Share them with us in the comments
What is Long Covid?
Long Covid is defined as symptoms that present 12 weeks after infection and that persist for at least 8 weeks. The most common symptoms being: Fatigue, Shortness of Breath and Cognitive Dysfunction. There will be an estimated 150 million cases of Long Covid cases worldwide as of 2022. Long Covid has the potential to significantly impact the lives of a large portion of the population making day to day activities difficult or near impossible. Although there are ways to reduce the risk factors in developing long covid, there aren’t many proven conventional medications to treat Long Covid once symptoms set in.
We now know that viral fragments, lingering spike protein and persistent inflammation are all likely features of Long Covid. This chronic state of immune activation leads to heart and blood vessel abnormalities, lung impairment, neurological injury and autoimmunity. Luckily, functional medicine practitioners have been at the forefront in developing protocols that work to resolve the aftermath of COVID-19 infection.
Mitochondrial Dysfunction
There is evidence of mitochondrial dysfunction in Long Covid cases as seen through disruption in fatty acid oxidation and altered lactate production. This would also partially explain the chronic fatigue of Long Covid. Functional medicine has a long history of developing protocols to address mitochondrial dysfunction. Many of the compounds used have been showing promise in treating Long Covid. For example, there is evidence of reduced levels of Coenzyme Q10 in COVID-19 infection. CoQ10 is an important compound in mitochondrial function and energy production. Supplementing with this compound along with other mitochondrial supportive nutrients (Niacin, N-Acetyl Cysteine, Alpha Lipoic Acid) have been helpful in treating Long COVID associated fatigue.
Chronic Inflammation
We also know that there is a wealth of data to suggest high levels of inflammatory markers in Long Covid sufferers. Conventionally, steroids such as prednisone have been used to effectively treat Long Covid symptoms. However, steroids can not be used indefinitely as there are significant side effects associated with long term usage. In Naturopathic and Functional Medicine we have evidence of a number of naturally derived compounds that work to treat Long Covid associated inflammation including: Curcumin, Resveratrol, Cannabinoids, Luteolin, Omega 3, and Black Cumin.
Immune System Abnormalities
We also know that there is immune system dysfunction in Long Covid as evidenced in abnormal T-cell behaviour. One of the most important compounds regulating immune function is vitamin D. There is strong evidence that having adequate vitamin D status prior to Covid infection is protective toward Long Covid and giving large doses of vitamin D to both active Covid-19 cases and Long Covid sufferers can be therapeutic.
Gastrointestinal Symptoms
Long Covid cases also seem to have a higher incidence of prolonged gastrointestinal symptoms and intestinal dysbiosis with organisms that increase inflammation. One of the best ways to treat intestinal inflammation is by promoting the growth of intestinal organisms that produce the short chain fatty acid Butyrate. Food that is high in fibre typically help to promote beneficial species of intestinal organisms. Oats, Apples, Onions, Asparagus, Broccoli, Whole grains, underripe bananas, Legumes, and Berries are some excellent foods shown to promote butyrate production.
Cannabinoids
Cannabinoids, and more specifically cannabidiol (CBD) has been shown to have some interesting mechanisms in the treatment of Long Covid. Strains of cannabis containing high levels of CBD have been shown to block spike protein from entering the cell (via ACE-2 receptors), modulate ACE-2 receptor density on cell surfaces (less doors of COVID to enter) and reduce inflammation. Therefore cannabinoids are very exciting compounds currently being investigated for use in Long Covid therapy.
Conclusions
Long Covid is a multifaceted chronic disease with effects on various physiological systems. Drugs with a narrow therapeutic scope are not going to be as effective as complex compounds that effect multiple physiological processes at the same time. This type of therapeutic synergy is a hallmark of naturally derived medicines and therefore functional medicine is going to play a pivotal role in dealing with this prevalent and highly complex disease state. In my Toronto practice I have had several cases of long covid that only began to resolve once a functional medicine protocol was put into place. So if you know someone who is suffering from Long Covid I recommend connecting them with a local Naturopathic Doctor or Functional Medicine Practitioner.
The mind body connection
The mind and body are closely connected through thousands of chemical messengers. When we have a mental experience the brain sets off a cascade of neurotransmitters and hormones that affects our body. For instance when we experience joy, our body produces the hormone oxytocin. Oxytocin reduces blood pressure, stress hormone, anxiety and promotes growth and healing. Conversely, when we experience an emotion like sadness this can raise stress hormone, increasing blood pressure and eliciting negative effects on the immune system. Psychotherapy can therefore have a big impact on the health of our body by modifying mental outlook and thus inducing positive chemical messengers to the rest our body. An example is cognitive behavioural therapy, which has well documented success in the treatment of depression, anxiety and stress. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/ 31004323/
We can also treat conditions of the mind through our body. In pharmaceutical medicine, drugs like anti-depressants can block the breakdown of the neurotransmitter serotonin. Serotonin is involved in mood and therefore in some individuals boosting serotonin activity can improve mood and decrease anxiety. However, some short falls of pharmaceutical medicine is that it can often cause unwanted side effects and have a narrow therapeutic range; meaning that too little may have no effect and too much can be deadly. There are also issues with dependancy and addiction.
On the other hand nutritional and herbal supplementation can be an effective treatment for depression, stress and anxiety without the same safety concerns as drugs.
Supplementation for depression
Depression is both a physical and emotional condition. We know that depression can impact the reproductive system, immune system and our nervous system. Nutritional deficiencies can arise as a result of long standing depression and can be a precursor in the development of a depressive condition. Deficiencies in vitamin B12, vitamin D and protein are associated with depression. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/ 23377209/ In my Toronto clinic we can identify and correct nutritional deficiencies and make a big impact on depressive symptoms.
There is also a lot to be said about the impact of chronic inflammation on brain and mental health. Research has shown that chronic inflammation can increase susceptibility to depression. https:// pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32553197/ At the Toronto clinic we treat inflammation using supplements such as curcumin, omega-3 fatty acids and cannabidiol (CBD). These supplements can improve depressive symptoms through modulation of inflammation.
Furthermore many natural health products like CBD can also impact neurotransmitters (brain messenger chemicals) directly associated with depression. Through the interaction of cannabinoid receptors, 5-HT1A (involved in serotonin regulation) and neurogenesis factors CBD can act similarly to an anti-depressant medication but with less potential for adverse effects. At the Toronto clinic I offer cannabis education and counselling when cannabinoids would benefit a patients condition.
Supplementation for Anxiety
Anxiety disorders are the most common mental illness in the United States effecting close to 20% of the population every year. While genetics play a significant role in the development of an anxiety disorder, biological and environmental factors are pivotal as well. We know that there are often disruptions in serotonin and dopamine, cortisol and adrenaline in anxiety syndromes. A common class of drugs used in the treatment of anxiety are the benzodiazepines (Xanax, Valium, Ativan etc…). Although these medications can be very effective, they often have significant side effects (drowsiness, depression, constipation). Benzodiazepines can also be difficult to stop once started. One of the most significant mechanisms in which anti-anxiety medications work is through the GABA receptor system.
GABA is an inhibitory neurotransmitter, meaning that it helps to calm the nervous system and muscular skeletal system. Benzodiazepines have a very strong effect on GABA receptors making them effective but also potentially dangerous.
Many nutraceutical compounds activate the GABA pathway but with a gentler effect than benzodiazepines. Pharma GABA (GABA produced by bacteria), Passionflower, St. Johns Wort, Taurine, 5-HTP and CBD all have well documented effects on GABA and Serotonin. At the Toronto clinic we use these compounds successfully in the treatment of anxiety syndromes with less potential for adverse effects.https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/ 11679026/
Supplementation for Stress
Every single human being experiences stress throughout their life. Stress can be a healthy natural process in the right circumstances and at the right time. Stress becomes pathological when it is experienced chronically and without appropriate instigation. Long lasting stress can have detrimental effects on multiple biological systems including the immune system, endocrine system (hormones) and cardiovascular system. https:// www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5137920/
There are no specific pharmaceutical interventions in the treatment of stress. Benzodiazepines are the most common class of drug prescribed for debilitating stress and as I mentioned in the section on anxiety, benzodiazepines can have significant side effects and issues with dependency.
Since there is a wide spectrum of factors that can cause stress a “one size fits all” approach is not always effective. The naturopathic approach is fundamentally holistic and therefore takes into account mental, emotional and physical stressors. For instance a change in work schedule may be contributing to sleep disruption, leading to insomnia, poor work performance and nutritional disruption.
Furthermore, there is an entire class of nutritional and herbal supplements called adaptogens. Adaptogens have the ability to modulate cortisol (stress hormone) preventing peaks and dips in cortisol levels throughout the day. Overtime treatment with adaptogens facilitate a more balanced cortisol output avoiding periods of hyperactivity and burnout. To my knowledge there are no pharmaceutical drugs that act in a similar way. Some common adaptogens are: Ashwagandha, Rodiola and Siberian Ginseng. Vitamins like Vitamin C and Magnesium can help support adrenal function further helping the body to avoid burnout in periods of prolonged stress. At the Toronto clinic I use these adaptogenic compounds in conjunction with other treatments to provide a safe and effective treatment plan for chronic stress.
The mind can be treated through the body. Pharmaceutical interventions can be effective but often come with safety concerns around adverse effects and dependancy. There are many safe and effective natural approaches to mental health conditions through supplementation. At my Toronto clinic we specialize in developing an individualized plan to help achieve your mental health goals.
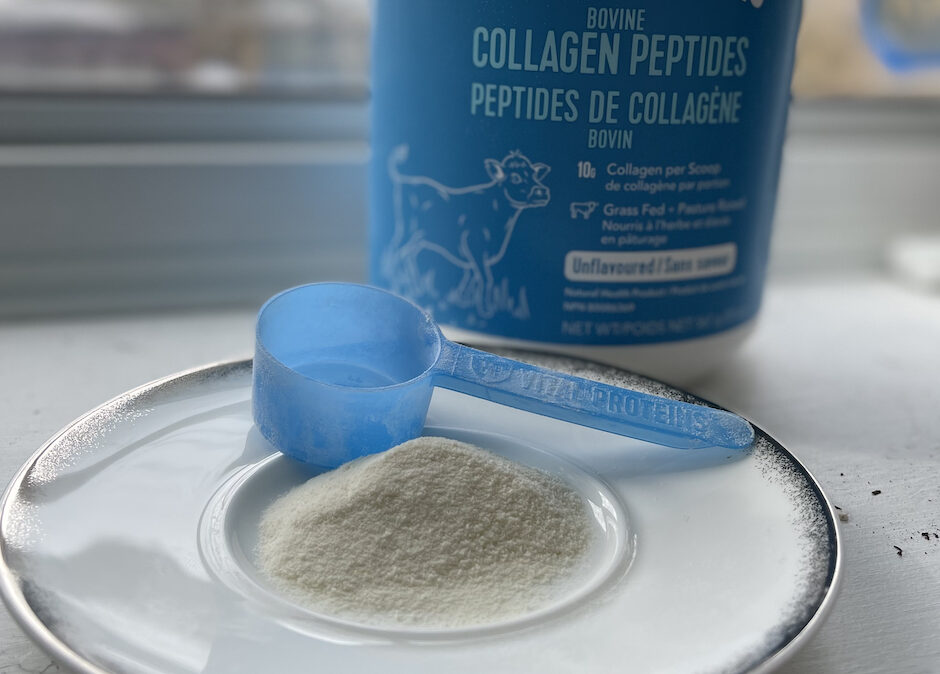
For the past 6-months I have been supplementing with collagen peptides in my morning coffee. I take relatively few daily supplements; Lions Mane mushroom for my brain, Vitamin D for my immune system and Collagen Peptides for my joints. I became focused on protecting my joints (especially my fingers, toes, knees and shoulders) a few years ago as I started training harder in rock climbing. I began to feel stiffness, soreness and occasionally pain after hard training sessions. I decided I needed to do something soon or I would lose the ability to climb at a relatively young age.
Instead of suppressing inflammation with compounds like curcumin, glucosamine and chondroitin I wondered if it would be possible to actually strengthen my tendons and ligaments. I had been aware of collagen supplementation through a number of patients taking it for hair and skin health. I had largely dismissed collagen as a beauty supplement and it was therefore not on my radar as a potential athletic enhancement.
Just over 6-months ago I had received a newsletter about of tendon health for climbers. The physiotherapist/climbing expert outlined specific exercises for warming up fingers and also mentioned the benefits of collagen supplementation for tendon health. At that moment I decided to re-visit the research on collagen, and I am glad I did!
Collagen peptides are small amino acid chains derived from collagen, which is the primary structural protein in ligaments, tendons, bones and skin. The research behind supplementing with collagen peptides seems to support three key areas.
Skin
A few studies, including randomized placebo controlled trials, have shown an improvement in skin moisture, elasticity and wrinkles with daily supplementation of Collagen Peptides. The daily dose ranged from 4-10 grams daily.
Osteoarthritis
Several studies have demonstrated a modest benefit in pain and function with daily supplementation of Collagen Peptides. Most studies focused on osteoarthritis (OA) in the knees but a couple also mention hip and hand. In general the improvement was modest (a little better than chondroitin) and took approximately 3-5 months to appear. Some studies used collagen peptides in combination with other compounds like chondroitin and hyaluronic acid. Most studies used a 10 gram daily dose.
Performance Enhancement
A great systematic review came out in 2021 that looked at the effects of collagen peptide supplementation on body composition, collagen synthesis and recovery from joint injury.
Five studies demonstrated a positive effect on reducing joint discomfort, knee pain , ankle and knee function and recovery from achilles tendinopathy. Those studies used 40 mg-10 grams per day over a 4-6 month period.
Four studies looked at the effects of collagen supplementation on body composition and muscle strength. The studies combined collagen supplementation (15 grams per day for 3-months) with resistance training.The studies, which were conducted on elderly men, active men and untrained pre-menopausal women, found an increase in fat free mass, a decrease in body fat percentage and an increase in hand grip strength.
Two studies assessed the effect of collagen supplementation on exercise performance and recovery from muscle soreness. The studies included recreationally active men, one used 3 grams per day for 6 weeks and the other used 20 grams per day for 7 days prior to intense exercise. There was a strong positive effect on pain with movement and muscle soreness.
Two studies assessed the effects of Collagen peptide supplementation on collagen synthesis. When taken 60min prior to exercise there was a significant increase in collagen synthesis markers following ingestion of 15 grams collagen enriched with vitamin C.
Conclusions
When it comes to preserving joint, ligament and tendon health for myself and my patients, collagen peptide supplementation is now a staple. The evidence in favour of collagen, along with a strong safety profile makes collagen peptides a valuable nutritional supplement in both sports medicine and anti-aging medicine. The recommended dose seems to be between 10-20 grams per day for 3-6 months.
References
Inoue N, Sugihara F, Wang X. Ingestion of bioactive collagen hydrolysates enhance facial skin moisture and elasticity and reduce facial ageing signs in a randomised double-blind placebo-controlled clinical study. J Sci Food Agric. 2016;96(12):4077-81.
Czajka A, Kania EM, Genovese L, et al. Daily oral supplementation with collagen peptides combined with vitamins and other bioactive compounds improves skin elasticity and has a beneficial effect on joint and general wellbeing. Nutr Res 2018;57:97-108.
Asserin J, Lati E, Shioya T, Prawitt J. The effect of oral collagen peptide supplementation on skin moisture and the dermal collagen network: evidence from an ex vivo model and randomized, placebo-controlled clinical trials. J Cosmet Dermatol. 2015;14(4):291-301
Sangsuwan W, Asawanonda P. Four-weeks daily intake of oral collagen hydrolysate results in improved skin elasticity, especially in sun-exposed areas: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. J Dermatolog Treat. 2020:1-6.
Benito-Ruiz P, Camacho-Zambrano MM, Carrillo-Arcentales JN, et al. A randomized controlled trial on the efficacy and safety of a food ingredient, collagen hydrolysate, for improving joint comfort. Int J Food Sci Nutr. 2009;60 Suppl 2:99-113.
Kumar S, Sugihara F, Suzuki K, Inoue N, Venkateswarathirukumara S. A double-blind, placebo-controlled, randomised, clinical study on the effectiveness of collagen peptide on osteoarthritis. J Sci Food Agric. 2015;95(4):702-7.
Trc T, Bohmová J. Efficacy and tolerance of enzymatic hydrolysed collagen (EHC) vs. glucosamine sulphate (GS) in the treatment of knee osteoarthritis (KOA). Int Orthop. 2011;35(3):341-8
Moskowitz RW. Role of collagen hydrolysate in bone and joint disease.Semin Arthritis Rheum 2000;30:87-99
Kalman DS, Schwartz HI, Pachon J, Sheldon E, Almada AL. A randomized double blind clinical pilot trial evaluating the safety and efficacy of hydrolyzed collagen type II in adults with osteoarthritis. FASEB Experimental Biology 2004 Abstracts, Washington DC, April 17-21, 2004; A90.
Amino Acids. 2021; 53(10): 1493–1506.Published online 2021 Sep 7. doi: 10.1007/s00726-021-03072-xPMCID: PMC8521576PMID: 34491424The effects of collagen peptide supplementation on body composition, collagen synthesis, and recovery from joint injury and exercise: a systematic review Mishti Khatri,1 Robert J. Naughton,1 Tom Clifford,2 Liam D. Harper, 1 and Liam Corr1
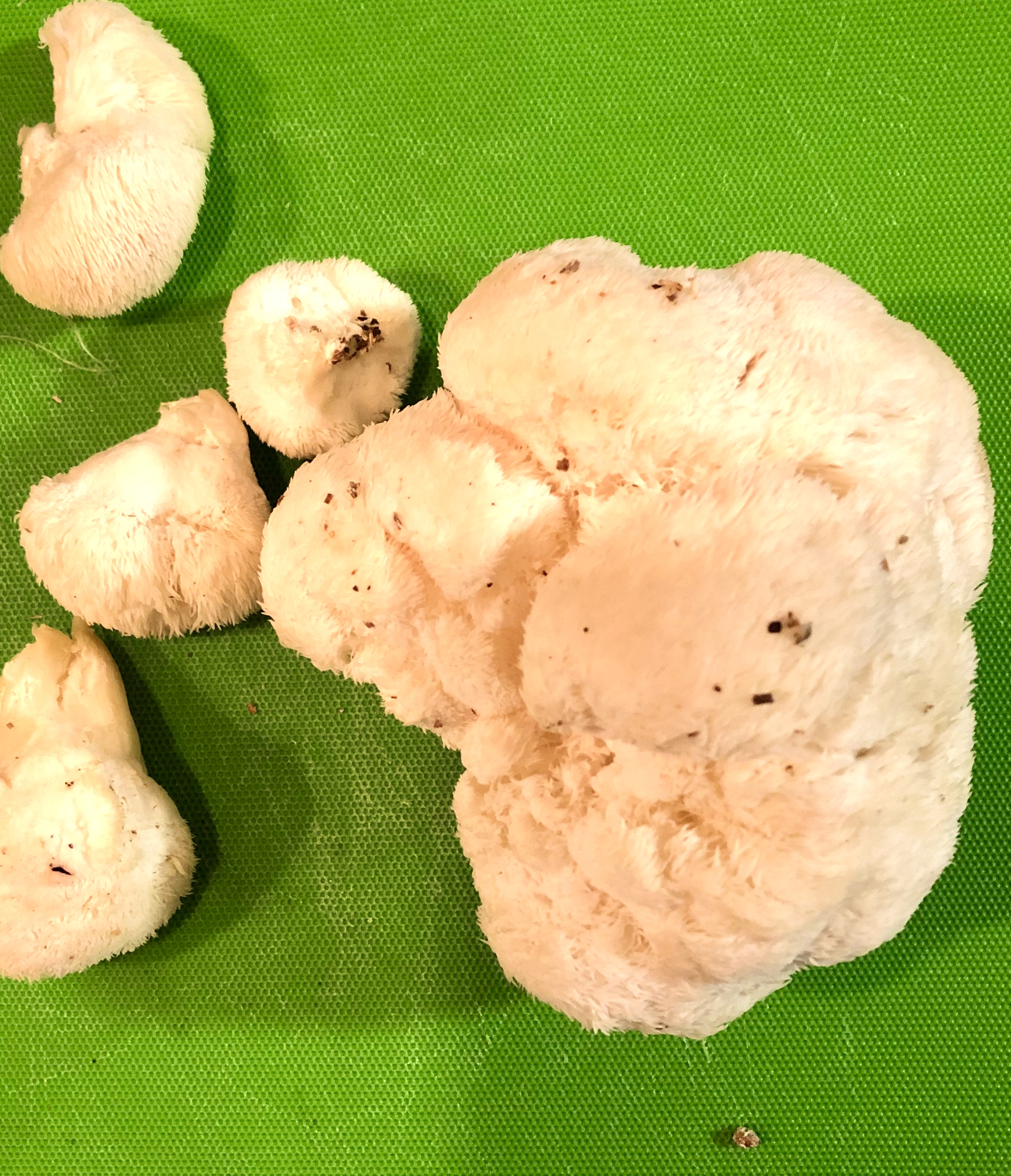
“Let food be thy medicine, and let medicine be thy food”; a famous quote from the Classical Grecian physician Hippocrates. Lions Mane mushrooms are a perfect embodiment of this philosophy; as delicious as it is therapeutic.
Lions mane (Hericium Erinaceus) is a white clumpy mushroom with long dangling spines that tends to grow in late summer/early fall on hardwoods.
I was first introduced to Lion’s Mane a few years ago when I had a few patients tell me they were using an extract of the mushroom to help with memory. Supplements that enhance brain activity, AKA Nootropics, have always tweaked my interest as one of my areas of clinical focus is in neurology. At first I thought that maybe this is the newest “superfood fad” but once I began to investigate the research on this mushroom my opinion quickly changed.
It was clear that Lions Mane had some legitimate therapeutic value in inflammation, the immune system, psychiatric conditions, cognitive enhancement, diabetes, heart disease, bowel disease and cancer.

Inflammation and Depression
A 2012 study demonstrated that Lions Mane mushroom contains several compounds that have moderate to high levels of antioxidant capacity. This translates into an anti-inflammatory effect in the body. A 2015 study demonstrated that participants who consumed Lions Mane had less depressive symptoms and improvements in blo-markers of depression which was attributed to it’s anti-inflammatory effects. Another study demonstrated that Lions Mane can enhance immune function possibly by reducing inflammation and oxidative stress.
Immune
Not only does Lions Mane help boost immune function by reducing oxidative stress, it also seems to benefit intestinal immune function. A study on mice revealed that some of the proteins in the mushroom help encourage the growth of beneficial bacteria in the gut.
Memory
Cognitive enhancement is the main reason that I see people taking this mushroom. It is possible that it does have some cognitive enhancement properties but all the research so far has been done on animals. One such study found that mice given a lion’s mane supplement had better object recognition and recognition memory. Other research suggests that Lions Mane may have the potential to prevent or treat conditions of cognitive decline like Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s disease.

Heart Health
Research on rats has demonstrated that Lions Mane may have cholesterol lowering effects and blood pressure lowering effects. Compounds in Lions Mane may help in the production of Nitric Oxide, which helps keep blood vessels relaxed.
Cancer
The antioxidant properties of Lions Mane may contribute to some anti-cancer effects seen in rat and in vitro studies. One in vitro study indicated that Lions Mane has activity against human leukemia cells. Another study showed that in mice, Lions Mane has activity against Liver, Colon and Gastric cancer cells.
Diabetes
After 4 weeks of Lions Mane supplementation, rats with diabetes had lower blood sugar levels than those who did not receive the mushroom. Diabetes can often result in life altering nerve damage. A 2015 study showed that diabetic rats given an extract of Lions Mane had reduced nerve pain and improved antioxidant activity after 6 weeks.

Digestive Health
I previously discussed how Lions mane can have anti-inflammatory effect of the digestive tract, as well as benefitting the growth of “good” intestinal bacteria. Another study demonstrated that Lions Mane has some interesting antimicrobial effects. Notably, Lions Mane seems to inhibit the growth of H-pylori, a bacteria responsible for close to 80% of stomach ulcers.
Nerve Repair
One of the most fascinating health benefits of Lions Mane came out of a rat study. Rats with nerve damage who were given daily extracts of Lions mane had quicker nerve cell regeneration than those who did not.
Culinary
Up until a few weeks ago I thought Lions Mane was an exotic mushroom that was only used therapeutically as a supplement. Recently, I found myself in a local Farmers Market and low and behold a mushroom farmer was selling fresh Lions Mane; I was amazed! I asked the farmer “how do I prepare this”? He told me to cut the mushroom in ½ inch slices and in a hot pan with butter, sear both sides. So, I bought some and followed his advice, and discovered that Lions Mane is absolutely delicious! It is now one of my favorite cooking mushrooms and I have since heard from many foodies and chefs that it is one of their favorites too. So let food be thy medicine everyone, and cook up some Lions Mane this fall!
Citations
Leonard, Jayne. “What are the benefits of lion’s mane mushrooms?.” Medical News Today. MediLexicon, Intl., 22 Oct. 2018. Web.
30 Oct. 2019. <https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/323400.php>
Leonard, J. (2018, October 22). “What are the benefits of lion’s mane mushrooms?.” Medical News Today. Retrieved from
https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/323400.php.
| Lion’s Mane Mushroom, <i>Hericium erinaceus</i> (Bull.: Fr.) Pers. Suppresses H<sub>2</sub>O<sub>2</sub>-Induced Oxidative Damage and LPS-Induced Inflammation in HT22 Hippocampal Neurons and BV2 Microglia. |
| Kushairi N, Phan CW, Sabaratnam V, David P, Naidu M. |
| Antioxidants (Basel). 2019 Aug 1;8(8). pii: E261. doi: 10.3390/antiox8080261. |
| PMID: 31374912 [PubMed] Free Article |
| Thirteen-Week Oral Toxicity Evaluation of Erinacine AEnriched Lion’s Mane Medicinal Mushroom, Hericium erinaceus (Agaricomycetes), Mycelia in Sprague-Dawley Rats. |
| Lee LY, Li IC, Chen WP, Tsai YT, Chen CC, Tung KC. |
| Int J Med Mushrooms. 2019;21(4):401-411. doi: 10.1615/IntJMedMushrooms.2019030320. |
| PMID: 31002635 [PubMed – indexed for MEDLINE] |
| In Vitro and In Vivo Inhibition of Helicobacter pylori by Ethanolic Extracts of Lion’s Mane Medicinal Mushroom, Hericium erinaceus (Agaricomycetes). |
| Wang G, Zhang X, Maier SE, Zhang L, Maier RJ. |
| Int J Med Mushrooms. 2019;21(1):1-11. doi: 10.1615/IntJMedMushrooms.2018029487. |
| PMID: 30806251 [PubMed – indexed for MEDLINE] |
| Dietary Supplementation of Lion’s Mane Medicinal Mushroom, Hericium erinaceus (Agaricomycetes), and Spatial Memory in Wild-Type Mice. |
| Rossi P, Cesaroni V, Brandalise F, Occhinegro A, Ratto D, Perrucci F, Lanaia V, Girometta C, Orrù G, Savino E. |
| Int J Med Mushrooms. 2018;20(5):485-494. doi: 10.1615/IntJMedMushrooms.2018026241. |
| PMID: 29953363 [PubMed – indexed for MEDLINE] |
| A Polysaccharide Isolated from Mycelia of the Lion’s Mane Medicinal Mushroom Hericium erinaceus (Agaricomycetes) Induced Apoptosis in Precancerous Human Gastric Cells. |
| Wang M, Zhang Y, Xiao X, Xu D, Gao Y, Gao Q. |
| Int J Med Mushrooms. 2017;19(12):1053-1060. doi: 10.1615/IntJMedMushrooms.2017024975. |
| PMID: 29431066 [PubMed – indexed for MEDLINE] |
| Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Ethanol Extract of Lion’s Mane Medicinal Mushroom, Hericium erinaceus (Agaricomycetes), in Mice with Ulcerative Colitis. |
| Qin M, Geng Y, Lu Z, Xu H, Shi JS, Xu X, Xu ZH. |
| Int J Med Mushrooms. 2016;18(3):227-34. doi: 10.1615/IntJMedMushrooms.v18.i3.50. |
| PMID: 27481156 [PubMed – indexed for MEDLINE] |
Cold and Flu season is here! Now that kids are back to school and the season is changing we should start thinking about preventing colds and flu. As a Naturopathic Doctor part of my job is counseling parents on safe and effective ways to treat and prevent colds and flu for the whole family. Here are 5 things that will help prevent colds and flu and can even help to ameliorate symptoms and shorten duration of an active infection.
-
Probiotics
Probiotics help boost the immune system – Studies have shown that probiotics affect immune cells throughout the body. When certain strains of probiotics are introduced into our intestine they help to repair intestinal cells and they boost production of antimicrobial substances. In one study, 326 children aged 3-5 years were randomly assigned to receive, in double-blind fashion, probiotic supplementation. Treatments were given twice per day in divided doses for 6 months, including the winter season. Compared with placebo, the probiotic group had the following results; fever reduction 53-73%, cough reduction 41-62%, decreased runny nose 28-59%, decreased need for antibiotics 68-82%, reduced absence from school 28-32%.
-
Elderberry
Elderberry extracts inhibit bacteria and viruses – Not only does elderberry syrup taste great, studies have shown that it inhibits the bacteria and viruses associated with common colds and the flu. One study demonstrated that an elderberry liquid extract possesses antimicrobial activity against both streptococci bacteria and influenza viruses. Another study looked at 312 air travellers flying from Australia to an overseas destination. Those travellers who took an elderberry extract before, during and after travel had fewer colds, less sick days and less symptoms.
-
Vitamin C
Vitamin C supports immune cells – Vitamin C is very important for optimal immune system functioning. Vitamin C helps immune cells get to where they need to be, kill pathogens effectively, protect the body from damage and clean up after battling infections. Studies have shown that adequate vitamin C in the blood helps prevent infections, is necessary to fight infections and helps with recovery. The recommended daily intake of vitamin C is 100-200mg/day; however during active infection, the metabolic demand increases and therefore the requirement for vitamin C is likely to be higher. Even in this day and age, vitamin C is the fourth leading nutrient deficiency in North America. Poor diet and increases in free radical exposure due to an unhealthy lifestyle may be contributing factors. Excellent sources of vitamin C are Broccoli, Citrus Fruits and Berries.
-
Zinc
Zinc is essential for immune system communication – The importance of zinc for proper immune function has been well established. Zinc deficiency undoubtedly causes immune system malfunction. The cells of our body are in constant communication. During infection there is a need for effective communication between immune cells in order to get rid of the “bad guys”. Communication happens in the form of chemical messengers and enzymes. Zinc is an essential component of these chemicals and enzymes. As with vitamin C, during active infection our requirement for zinc is likely to increase. Studies have shown that Zinc supplementation during infection can shorten the duration of the illness. Excellent dietary sources of zinc include: Meat, Shellfish, Legumes, Nuts and Seeds. Supplementation may be important with a vegan or vegetarian diet.
-
Vitamin D
Vitamin D is the supervisor of the immune system –Vitamin D has many functions in the body, and receptors for vitamin D can be found on many different tissues. One important function for vitamin D is in the modulation of our immune system. Studies have suggested that vitamin D is able to both calm down and rev-up the immune system according to what our body needs it to do. This is why Vitamin D is thought to be as important in autoimmune disorders as it is in infections.
Vitamin D deficiency can cause the immune system to behave erratically. Unfortunately in Canada we have one of the highest incidences of vitamin D deficiency in the world. Our primary source of vitamin D is from sunlight and therefore supplementation becomes important especially during the winter months. Studies have shown that there is a higher incidence of upper respiratory tract infections in athletes who are deficient in the vitamin and who train in the wintertime. Supplementation had preventative and symptom reducing effects. Aside from sunlight, some dietary sources of vitamin D are: fortified foods, fatty fish, beef liver, egg yolks and cheese.
Even vitamins and minerals at high dosages can be dangerous, especially in children. It is always recommended to consult with a health care professional, such as a Naturopathic Doctor, before supplementing on your own.
[button size=”btn-large” link=”https://doctorshawn.ca/contact-us/” target=”_blank” ]Book an appointment today![/button]
Leyer, GJ et al. Probiotic effects on cold and influenza-like symptom incidence and duration in children. Pediatrics 2009; 124-179. Walker, WA. Mechanisms of action of probiotics. Clin Infect Dis. 2008; 46 (Suppl2): S87-91.
Curr Opin Gastroenterol. 2011 October ; 27(6): 496–501. doi:10.1097/MOG.0b013e32834baa4d. Probiotics and immune health Fang Yana and D.B. Polkb,c,d
Elderberry Supplementation Reduces Cold Duration
and Symptoms in Air-Travellers: A Randomized,
Double-Blind Placebo-Controlled Clinical Trial Evelin Tiralongo 1,2, *, Shirley S. Wee 2,3 and Rodney A. Lea 4 Received: 8 February 2016; Accepted: 18 March 2016; Published: 24 March 2016
Krawitz et al. BMC Complementary and Alternative Medicine 2011, 11:16
http://www.biomedcentral.com/1472-6882/11/16
Inhibitory activity of a standardized elderberry
liquid extract against clinically-relevant human
respiratory bacterial pathogens and influenza A
and B viruses Christian Krawitz1†, Mobarak Abu Mraheil1†, Michael Stein2, Can Imirzalioglu1, Eugen Domann1, Stephan Pleschka2*,
Torsten Hain1*
Vitamin C and Immune Function Anitra C. Carr 1, * and Silvia Maggini 2
1 Department of Pathology, University of Otago, Christchurch, P.O. Box 4345, Christchurch 8140, New Zealand
2 Bayer Consumer Care Ltd., Peter-Merian-Strasse 84, 4002 Basel, Switzerland; silvia.maggini@bayer.com* Correspondence: anitra.carr@otago.ac.nz; Tel.: +643-364-0649 Received: 21 September 2017; Accepted: 31 October 2017; Published: 3 November 2017
Biofactors. 2014 Jan-Feb;40(1):27-40. doi: 10.1002/biof.1114. Epub 2013 Jun 27.Zinc signals and immune function. Haase H1, Rink L.
Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013 Jun 18;(6):CD001364. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD001364.pub4. Zinc for the common cold.
Vitamin D3 Supplementation Reduces the Symptoms
of Upper Respiratory Tract Infection during Winter
Training in Vitamin D-Insufficient Taekwondo
Athletes: A Randomized Controlled Trial Hyun Chul Jung 1 , Myong-Won Seo 2 , Sukho Lee 3 , Sung Woo Kim 2 and Jong Kook Song 2, * 1 Department of Kinesiology, College of Health Sciences, University of Louisiana at Monroe, 700 University
Avenue, Monroe, LA 71209, USA; jung@ulm.edu
2 Department of Taekwondo, College of Physical Education, Kyung Hee University, 1732 Deokyoungdaero, Giheung-gu, Yongin-si, Gyeonggi-do 17014, Korea; smilly1004@khu.ac.kr (M.-W.S.); kswrha@khu.ac.kr (S.W.K.)
3 Department of Counseling, Health, and Kinesiology, College of Education and Human Development,Texas A&M University-San Antonio, One University Way, San Antonio, TX 78224, USA; slee@tamusa.edu* Correspondence: jksong@khu.ac.kr; Tel.: +82-31-201-2708 Received: 2 August 2018; Accepted: 10 September 2018; Published: 14 September 2018
Mechanisms Underlying the Regulation of Innate and
Adaptive Immunity by Vitamin D Ran Wei and Sylvia Christakos *
Received: 25 June 2015 ; Accepted: 15 September 2015 ; Published: 24 September 2015 Department of Microbiology, Biochemistry and Molecular Genetics, New Jersey Medical School, Rutgers, the State University of New Jersey, 185 South Orange Ave, Newark, NJ 07103, USA; weira@njms.rutgers.edu
* Correspondence: christak@njms.rutgers.edu; Tel.: +973-972-4033; Fax: +973-972-5594