Mouth breathing can seem like a small issue, but it can actually lead to a range of problems, from bad breath and difficulty sleeping to developmental issues in children. If you notice that your child is constantly breathing through their mouth, it’s important to take action. Here are 5 ways to combat mouth breathing in kids and ensure that your child is breathing properly.
1. Identify the Root Cause
The first step to combating mouth breathing is determining the root cause. Some common causes include allergies, enlarged tonsils or adenoids, or a deviated septum. Once you identify the cause, you can work with your child’s pediatrician to formulate a treatment plan. Treatment may involve medication, surgery or lifestyle changes like avoiding certain foods or environmental allergens.
Chronic nasal congestion may be a cause of mouth breathing in children. If structural and allergic causes have been ruled out, it may be a good idea to test for food sensitivities. Food sensitivities develop as a result of a slightly different immune response than allergies. A naturopathic doctor or functional medicine doctor can requisition a blood test that will identify any food sensitivities in your child. Sensitivities will often resolve after 3-months of abstinence at which time these foods may be re-introduced into the diet.
2. Practicing Breathing Exercises
Teaching kids proper breathing techniques can help them switch from mouth breathing to breathing through their nose. Encourage them to take long, deep breaths through their nose and exhale slowly through their mouth. You can also make it into a fun game by challenging them to see how long they can hold a deep breath in their nose or how long they can exhale.
A fantastic resource for nasal breathing exercises as well as some of the scientific literature around mouth breathing vs. nasal breathing can be found through the Buteyko Clinic
3. Promote Good Sleep Hygiene
Many kids breathe through their mouth while sleeping, so it’s crucial to establish good sleep hygiene to prevent mouth breathing before it starts. Make sure your child is sleeping on their back or side, as sleeping on the stomach can encourage mouth breathing. You may also consider using a humidifier, which can help to keep sinuses moisturized and reduce inflammation.
Here is a checklist for establishing good sleep hygiene in kids:
✅ Establish a consistent bedtime routine and consistent wake-up time every day.
✅ Avoid caffeinated drinks, large meals, and vigorous exercise late in the day.
✅ Create a calm, relaxing atmosphere in the bedroom by dimming lights and avoiding screens.
✅ Avoid napping during the day. If naps are necessary, keep them short (15-30 minutes) and at the same time each day.
✅ Keep bedroom temperature comfortable. A cool but not cold room of around 65 degrees is ideal for sleep.
✅ Make sure your child’s mattress is comfortable and supportive to ensure quality rest.
✅ Exercise regularly, although not too close to bedtime as this can make it harder to fall asleep quickly.
✅ Encourage your child to find activities that help them relax before bedtime such as reading or taking a warm bath or shower in preparation for sleep
4. Maintain Proper Oral Hygiene
Mouth breathing can cause dry mouth, which can lead to a range of oral health problems. Encourage your child to brush their teeth twice daily and to floss regularly to remove any debris that may have accumulated between their teeth. Also, make sure they stay hydrated so that their mouth stays moist and saliva can flow normally.
5. Be a Positive Role Model
Lastly, it’s important to lead by example. Kids are extremely observant, so if they see their parents breathing through their mouth, it can become normalized. Pay attention to your own breathing habits and make sure you practice good nasal breathing techniques in front of your kids. You can even lead by example by doing breathing exercises or attending yoga classes together.
Conclusion:
Mouth breathing may seem like a small issue, but it can lead to a range of problems for kids. By taking action early and addressing the root cause, you can help your child learn better breathing techniques and combat mouth breathing. Encouraging proper nasal breathing techniques, practicing good sleep hygiene, promoting oral health, and being a positive role model are all excellent strategies for combatting mouth breathing in children. If you’re worried about your child’s breathing habits, talk to their naturopath or pediatrician to determine the best course of action.
As parents, we all want the best for our children, and that includes making sure they’re getting the nutrition they need to grow up healthy and strong. Proper nutrition is crucial to a child’s physical and cognitive development, and it can be challenging to navigate the world of childhood nutrition. But don’t worry; I’ve got you covered. In this brief guide, I will discuss the essential nutritional requirements for kids.
1. Carbohydrates
One of the most critical components of a child’s diet is carbohydrates. They give kids energy, so it’s essential to choose the right carbs – complex carbohydrates are the way to go. These are found in whole grains, fruits, and vegetables, and they provide kids with long-lasting energy throughout the day. Avoid processed or refined carbohydrates, like white bread or sugary cereals, as these can cause an energy crash later in the day.
The amount of carbohydrates that kids need for optimal health depends on their age, gender, and physical activity level. However, as a general guideline, the American Academy of Pediatrics recommends that children between the ages of 4 and 18 should get 45-65% of their daily calories from carbohydrates. For most children, this translates to about 130-200 grams of carbohydrates per day. Once again it is important to note that not all carbohydrates are created equal, and kids should focus on getting carbohydrates from nutritious sources such as: fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and legumes rather than from processed or sugary foods.
2. Protein
Growing children need plenty of protein, as it is essential for building and repairing tissues. Protein can be found in a variety of foods, such as meats, beans, eggs, and dairy products. You should aim to include a source of protein in each meal, but be mindful of focusing on lean sources, like skinless chicken, fish, legumes and soy to keep saturated fats to a minimum.
The amount of protein that kids need for optimal health varies depending on their age, gender, and physical activity level. However, as a general guideline, the American Academy of Pediatrics recommends that children between the ages of 4 and 13 should get about 0.95 grams of protein per kilogram of body weight per day, while children between the ages of 14 and 18 should get about 0.85 grams of protein per kilogram of body weight per day.
Good sources of protein for kids include lean meats, poultry, fish, eggs, dairy products, beans, legumes, and soy products. It’s important to encourage kids to eat a variety of protein-rich foods to ensure that they are getting all of the essential amino acids that their bodies need for growth and development. In general, it’s best to focus on getting protein from whole foods rather than from powders or supplements.
3. Fats
It’s important to include some healthy fats in a child’s diet, as they provide essential fatty acids that the body needs for growth and development. Some good sources of healthy fats include nuts, seeds, oily fish, and avocados. However, it’s essential to limit saturated fats, found in things like cheese and fried foods, as they can increase the risk of heart disease later in life.
The amount of fat that kids need for optimal health also depends on their age, gender, and physical activity level. However, as a general guideline, the American Academy of Pediatrics recommends that children between the ages of 1 and 3 years old should get about 30-40% of their daily calories from fat. Children between the ages of 4 and 18 years old should get about 25-35% of their daily calories from fat.
It’s important to note that not all fats are created equal, and kids should focus on getting their fats from healthy sources such as: nuts, seeds, olive oil, avocado, fatty fish, and dairy products like milk, cheese, and yogurt. These foods are rich in essential fatty acids, vitamins, and minerals that are important for growth and development. Trans fats and saturated fats, which are found in fried foods, bakery products, and high-fat meats, should be limited as much as possible as they increase the risk of heart disease and other chronic health conditions.
It’s important to also remember that fat provides more calories per gram than carbohydrates or protein, so portion control is key. Encouraging kids to eat a balanced and varied diet that incorporates healthy sources of fat is important for their overall health and well-being.
4. Vitamins and Minerals
Kids need plenty of vitamins and minerals to stay healthy and strong, and a varied diet should provide them with most of what they need. Encourage your child to eat a wide variety of fruits and vegetables, as these are excellent sources of essential vitamins and minerals. It’s also a good idea to include a daily multivitamin specifically formulated for children, which can help fill in any nutritional gaps in their diet.
Common vitamin and mineral deficiencies in kids:
-
Vitamin D: Vitamin D is essential for strong bones and teeth, as well as for overall health. Kids who get limited exposure to sunlight or who have a diet low in vitamin D-rich foods such as fatty fish, egg yolks, and fortified milk may be at risk for vitamin D deficiency.
-
Iron: Iron is critical for the production of red blood cells, which carry oxygen throughout the body. Kids who don’t get enough iron in their diet may be at risk for anemia, which can cause fatigue, weakness, and other health problems. Good sources of iron include lean meats, beans, whole grains, and fortified breakfast cereals.
-
Calcium: Calcium is essential for building strong bones and teeth as well as for muscle function and nerve transmission. Kids who don’t get enough calcium may be at risk for weakened bones and teeth. Good sources of calcium include dairy products, leafy green vegetables, and fortified products such as orange juice and tofu.
-
Vitamin C: Vitamin C is important for maintaining a healthy immune system and for the absorption of iron from plant-based foods. Kids who don’t get enough vitamin C in their diet may be at risk for a weakened immune system and a higher risk of infections. Good sources of vitamin C include citrus fruits, berries, kiwi, and vegetables such as peppers and broccoli.
-
Vitamin A: Vitamin A is critical for healthy vision, skin, and immune function. Kids who don’t get enough vitamin A in their diet may be at risk for vision problems, skin issues, and an increased susceptibility to infections. Good sources of vitamin A include carrots, sweet potatoes, dark leafy greens, and fortified foods such as milk and cereal.
-
Magnesium: Another common nutrient deficiency in kids is magnesium. Magnesium is involved in more than 300 enzymatic reactions in the body and is essential for healthy bone development, muscle function, and heart health. Good sources of magnesium include whole grains, nuts, seeds, legumes, leafy green vegetables, and fortified foods such as breakfast cereal. Kids who don’t get enough magnesium in their diet may be at risk for weaker bones, cardiovascular issues, and muscle weakness or cramping. While magnesium deficiencies are rare, kids who follow restrictive diets (such as vegan or low-carb diets) or who have certain health conditions (such as type 2 diabetes or gastrointestinal disorders) may be at an increased risk.
5. Hydration
Finally, it’s crucial to ensure that kids are drinking enough water. Children are more likely to become dehydrated than adults because they have a higher surface area to volume ratio, which means they lose more fluids through their skin. Encourage your child to drink water instead of sugary drinks, and make sure they’re getting enough fluids throughout the day, especially during physical activity.
The amount of water that kids need for optimal health depends on their age, sex, size, and activity level.
Recommendations:
-
Infants aged 0-6 months need about 1 liter of water per day, which is primarily obtained through breast milk or formula.
-
Infants aged 6-12 months need about 1.5 liters of water per day, which is primarily obtained through breast milk or formula and may be supplemented with small amounts of water.
-
Children aged 1-3 years need about 1.3 liters of water per day, which can come from water, milk, and other fluids as well as from the water content of foods.
-
Children aged 4-8 years need about 1.7 liters of water per day, which can come from water, milk, and other fluids as well as from the water content of foods.
-
Children aged 9-13 years need about 2.4 liters of water per day for boys and 2.1 liters of water per day for girls, which can come from water, milk, and other fluids as well as from the water content of foods.
-
Adolescents aged 14-18 years need about 3.3 liters of water per day for boys and 2.3 liters of water per day for girls, which can come from water, milk, and other fluids as well as from the water content of foods.
It’s important to note that these recommendations are general guidelines, and individual needs may vary based on factors such as temperature, humidity, and physical activity level. Encouraging kids to drink water and other healthy beverages throughout the day and eat foods with high water content such as fruits and vegetables is important for their overall health and well-being.
Conclusion
Nutrition is a vital component of a child’s health and wellbeing, and as parents, it’s our responsibility to ensure they’re getting the nutrients they need to grow up healthy and strong. The guidelines I’ve discussed here are just a starting point, and it’s always best to consult with a pediatrician, naturopathic pediatrician or registered dietitian to determine the specific nutritional needs of your child. By providing a varied diet that includes complex carbohydrates, lean proteins, healthy fats, and plenty of vitamins and minerals, we can help our children reach their full potential, both physically and mentally. So, go ahead and nourish your child’s body – and mind – with the power of good nutrition!
When it comes to treating constipation in children, parents often feel overwhelmed and may not know where to start. Constipation can be a serious health concern for kids if left untreated, so the good news is that there are a number of natural approaches that can help bring relief. With some dietary changes, supplementation, and lifestyle adjustments, you can create a custom treatment plan designed specifically for your child’s needs. In this blog post we will discuss these different methods so that you have all the information you need when considering what type of approach might work best for your little one!
Overview of Constipation in Kids
Constipation in kids can be a very concerning issue. It can cause discomfort and irritation, as well as interfere with appetite, sleep, and overall health. Constipation can be caused by inadequate diets, lack of exercise, anxiety, and other factors. Parents should ensure their children maintain a balanced diet that includes fiber-rich foods such as vegetables, fruits, legumes, and whole grains. Increasing physical activity is also important for keeping the digestive system healthy. Regular exercise also helps alleviate stress and consequently reduce constipation-causing anxiety among children. Additionally, parents should make sure kids have enough rest to keep their bodies relaxed thus preventing constipation from developing in the first place. If dietary changes and lifestyle adjustments do not improve constipation symptoms then supplementation may be necessary in order to restore regular bowel movements again.
Causes of Constipation in Children
Constipation in children is a common complaint but, fortunately, there are many natural and effective approaches to treating it. Diet is often the primary culprit behind constipation in kids; foods high in fats, processed carbohydrates and protein can slow digestion, while regular exercise and an increase of fibre has been proven to stimulate proper elimination. In addition, food sensitivities and levels of anxiety should not be ignored: both can have a significant effect on digestive health. By addressing diet and other potential lifestyle factors with these helpful tips, children suffering from constipation will eventually experience relief and have their digestive systems back up to speed.
Dietary Changes to Help Treat Constipation in Kids
Eating the right foods and drinks is a natural, effective way of relieving constipation in kids. Soluble fibre helps to soften stool by absorbing water and keeping it in the gut longer. Oatmeal, legumes, berries, chia, nuts and seeds are all sources of soluble fibre. Insoluble fibre adds bulk to stools and increases the frequency at which they can pass through your child’s gut. Foods rich in insoluble fibres include wholegrain cereals, wheat bran, vegetables and fruit skins. Alongside fibre-rich foods, be sure that your child is staying hydrated with plenty of water throughout the day. Two liters of fluids in the first 10 hours of the day is recommended. Lastly, adding prebiotic fibres such as onions, garlic, green bananas, apples or asparagus to their meals can also help them treat their constipation naturally by encouraging healthy bacteria growth in the gut.
Natural Remedies for Constipation in Children
Constipation in children can be distressing and uncomfortable. Fortunately, there are a range of natural remedies that can help alleviate the problem, such as massage, dietary changes and supplementation, acupuncture, and herbal remedies. Massage on the abdomen can help to relieve constipation by providing gentle stimulation of digestive organs. Dietary changes should include increased intake of fiber-rich foods such as fruits, vegetables and whole grains to prevent future bouts of constipation in your child. Supplementation with probiotics may also be beneficial in re-establishing healthy bacterial balance and restoring regularity within the gut flora. Acupuncture has been used for centuries for its restorative qualities and treating various aches, pains and bodily ailments including constipation. Herbal remedies are also available such as chamomile tea or lemon balm to help promote digestion.
Supplements for Constipation Relief in Kids
For constipation relief in children, natural supplementation may be an effective approach. Magnesium citrate is one of the most commonly used supplements to support regular and healthy elimination in kids. Butyrate, sunfibre, FOS and acacia are also helpful for improving stool consistency. Psyllium husk is a great source of soluble fibre which helps keep things moving along smoothly. Probiotics like Lactobacillus reuteri or Bifidobacterium infantis are beneficial in keeping beneficial bacteria levels balanced in the intestines. These methods may offer gentle but potent relief for constipation sufferers without harsh side effects associated with over-the-counter medications.
When to See a Doctor for Treatment of Constipation in Children
While constipation in kids is often treated with natural approaches, at times parents should seek medical attention. If your child has a bloody stool, complains of pain, or has not had a bowel movement in 4 days, it’s time to make an appointment for your child to see a doctor. Mucus and streaks in the stool can also be signs of more serious underlying issues that require professional care. Additionally, if you observe any hemorrhoids near the anus, then it is recommended that you take your child to the doctor right away.
Constipation can be a difficult issue for kids to deal with, causing discomfort and pain. Thankfully, there are many potential treatments that can help, such as dietary changes and natural processes like supplementation. If you have a child struggling with constipation, it’s important to keep track of their diet, identify any potential issues in their environment or recent lifestyle changes that might trigger the problem, and look into different supplements that may provide relief. However, if all else fails and you still can’t find an effective solution to the problem, it’s best to seek medical advice from your doctor. I hope that this blog post gave you more insight into the causes and treatments of constipation in children so that you’ll know what to do should your own little one start having issues. For more information or to book an appointment regarding constipation relief in kids, please contact me – I’m always here to help!
Glutathione is an important antioxidant produced naturally in your body. It helps to protect cells from damage, preserve energy levels, and improve overall health. Recently, glutathione infusions have become increasingly popular as a way to give your body an extra dose of this essential antioxidant. But what is the science behind it? Let’s take a closer look at glutathione infusion and its potential benefits for your health.
What is Glutathione?
Glutathione is an antioxidant found in all cells in your body and plays an important role in many biological processes. It acts as a detoxifying agent, helping to rid the body of toxins such as heavy metals and other pollutants. Additionally, glutathione helps to regulate cell growth, DNA repair, immune system responses, and antioxidant activity. In short, having sufficient amounts of glutathione in your system allows for optimal functioning of all these processes.
The Benefits of Glutathione Infusions
Although you can get some glutathione through diet or supplements, one of the best ways to increase your levels of this powerful antioxidant is through a glutathione infusion. An infusion involves injecting a concentrated solution of glutathione directly into the bloodstream. This ensures that the maximum amount of this nutrient is delivered quickly and efficiently into the body where it can be put to immediate use.
Studies have shown that these infusions can help reduce inflammation caused by oxidative stress and improve detoxification pathways in the body. Some research has even suggested that regular infusions may help improve symptoms associated with chronic illnesses like diabetes and Parkinson’s disease.
Glutathione infusions are also commonly used as part of anti-aging treatments since they help to reduce wrinkles and dark spots on skin due to their ability to reduce oxidative stress from ultraviolet radiation exposure. In addition to providing aesthetic benefits, these infusions may also help boost energy levels due to their ability to restore depleted nutrient stores in the body.
Glutathione and Parkinson’s Disease
Several studies have looked into Glutathione’s potential for treating Parkinson’s disease, a chronic neurodegenerative disorder characterized by motor and cognitive impairment.
A study published in 2015 that looked at both animal models and human clinical trials found that intravenous glutathione could provide symptomatic relief when used as an adjunct to conventional treatments. This research showed that it was safe, well-tolerated, and effective at reducing motor symptoms such as rigidity and bradykinesia.
More recently, a 2018 systematic review of clinical evidence found that using glutathione injections in combination with levodopa was significantly more effective than standard treatment alone. The results suggest that glutathione may help alleviate the motor symptoms associated with Parkinson’s while also potentially mitigating side effects from traditional medications.
Overall, several studies have shown promising findings indicating that intravenous glutathione can improve motor symptoms associated with Parkinson’s disease. As more research is conducted, it may become an increasingly viable option for patients seeking additional treatment options.
Glutathione in aesthetic and anti-aging medicine
Intravenous glutathione has become a popular choice for aesthetic and anti-aging applications in recent years. Research has suggested that it may be a safe and effective way to improve skin complexion, reduce signs of aging, and increase overall appearance.
A 2017 study from the University of Messina looked at the use of glutathione injections as an anti-aging treatment for the face and neck. The study found that using intravenous glutathione was an effective means of reducing wrinkles and improving skin texture, elasticity, tone and firmness. It also appeared to have some protective effects against UV radiation-induced damage such as pigmentation, inflammatory reactions, and skin atrophy.
In addition to its potential for treating the visible signs of aging, glutathione therapy has also been studied for its ability to correct pigmentation issues such as melasma and hyperpigmentation. A 2008 case series from Saudi Arabia showed that a combination of oral doses and topical application of glutithione could lead to significant improvement in facial discoloration over time.
Overall, there is growing evidence suggesting that intravenous glutathione can have beneficial effects on aesthetic medicine when used correctly. While more research is needed to confirm its efficacy in this area, it appears to offer promising results when used in conjunction with other treatments.
Glutathione and Multiple Sclerosis
Multiple sclerosis (MS) is an autoimmune disorder in which the body’s own immune system attacks and damages nerve cells. Recent research has suggested that glutathione may have potential for treating MS, as it is known to possess anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties.
A 2006 study from Belgium explored the effects of intravenous glutathione on MS patients who had previously failed to respond to conventional therapies. After 8 weeks of treatment with glutathione, researchers found that the majority of patients experienced significant improvements in their physical symptoms. Notably, these improvements were sustained during 12 months of follow up.
More recently, a 2017 systematic review looked at the use of intramuscular or intravenous glutathione injections in combination with interferon beta-1a for treating MS relapses. The results showed that this approach was more effective than just using interferon alone, resulting in better control of symptoms such as motor weakness and visual impairment.
Overall, while further research is needed to fully evaluate its potential, there is evidence suggesting that glutathione injections may be a safe and effective treatment option for certain types of MS-related symptoms. In particular, they appear to be beneficial when used as an adjunct therapy alongside existing medications.
Glutathione and Diabetes
Glutathione has long been studied for its potential role in treating diabetes. Research has suggested that it may be effective at reducing oxidative stress and inflammation, both of which are associated with the development of type 2 diabetes.
In a 2002 study from the University of Modena, researchers looked at the effects of intravenous glutathione injections on 42 diabetic patients. After 12 weeks of treatment, participants had significantly improved their blood sugar levels, as well as their lipid profile parameters. Moreover, 82% of them experienced an improvement in back pain and other physical symptoms.
A more recent 2011 study examined the effects of oral supplementation with glutathione on diabetic patients who had previously failed to respond to insulin therapy. The results showed that those receiving glutathione achieved better glycemic control compared to those receiving just insulin treatment alone. Additionally, they had improved scores on measures such as body mass index (BMI) and waist circumference.
Overall, while more research is needed to fully understand its potential in this area, there is evidence suggesting that glutathione may be beneficial in managing some of the symptoms associated with diabetes. In particular, it appears to offer promising results when used together with conventional therapies such as insulin injections or oral anti-diabetic drugs.
Conclusion
Glutathione infusions are becoming increasingly popular around the world for the health benefits it provides. Results have been particularly impressive when used to treat conditions such as Parkinson’s Disease, Anti-aging, multiple sclerosis and diabetes. Despite this, it is recommended that potential users only seek experienced healthcare professionals who can accurately prescribe the correct dose for them. We know that glutathione infusions provide substantial outcomes but it must be taken responsibly, in order to reach its full efficacy. At the very least, we recommend doing research prior to embarking on any type of treatment journey. To discover more information about our services and procedures involved in administering glutathione infusions please don’t hesitate to contact us today – we’d be more than happy to answer any questions or queries you may have!
Sources
Sharma V., et al., “Intravenous administration of reduced glutathione: A potential approach for therapy of patients with Parkinson’s Disease,” Neurochem Res (2015), doi: 10.1007/s11064-015-1510-6
Jubinsky P., et al., “Glutathione Therapy for Parkinson’s Disease: A Systematic Review,” Oxidative Medicine & Cellular Longevity (2018), doi: 10.1155/2018/1283082
De Keyser J., et al., “Intravenous glutathione in multiple sclerosis,” Neurology (2006), doi: 10.1212/01.wnl.0000232530.30045.bd
Batocchi AP., et al.,”Glutathione plus Interferon Beta-1a Versus Interferon Beta-1a Monotherapy for Multiple Sclerosis Relapses: A Systematic Review,” Neurol Clin Pract (2017), doi: 10.1097/ncp.0000000000000455
Cogliandro AF., et al., “Glutathione iv infusion: An innovative tool for antiglycation strategy,” J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol (2017), doi: 10.1111/jdv.14146
Almutairi A., et al., “Oral Glutathione as a Novel Treatment Modality for Melasma,” Dermatol Res Pract (2008), doi: 10.1155/2008/420464
Mocchegiani E., et al., “Oxidative Stress Parameters in Diabetics Before and After Intravenous Glutathione Therapy,” Free Radic Res (2002), doi: 10.1080/1071576021000051371
Kumar AK., et al.,”Metabolic Effects of Oral Glutathione Therapy in Type 2 Diabetics Not Responding to Sulfonylurea Drugs,” Nutrition & Metabolism (2011), doi: 10.1186/1743-7075-8-71
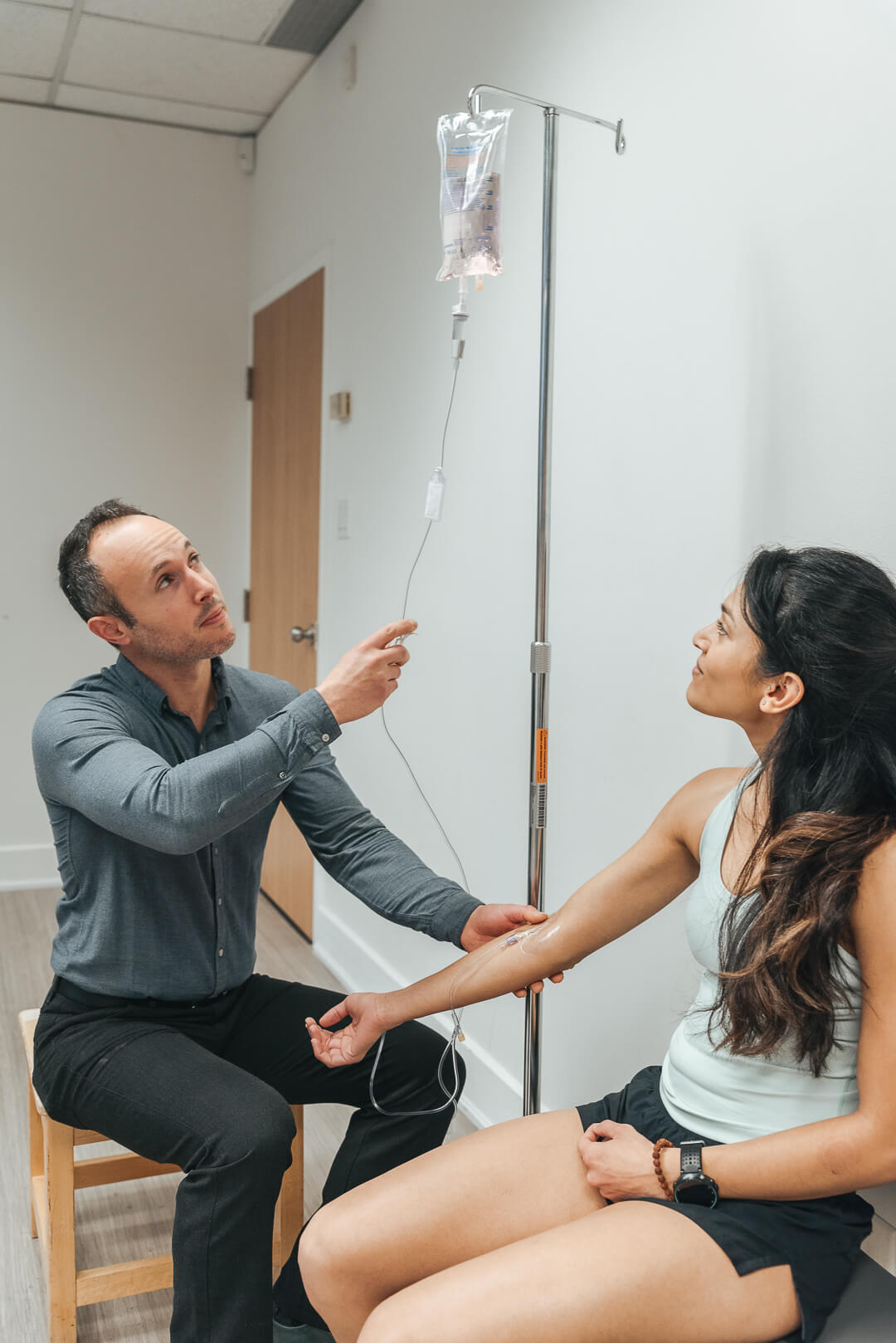
Intro to common IV therapies
Intravenous therapies such as The Myers Cocktail and High Dose Vitamin C have been used to treat a variety of health conditions for many years. A growing body of research is showing the potential benefits of using these therapies to improve the lives of patients with chronic illness.
Studies have shown that the Myers Cocktail can help improve symptoms related to fibromyalgia, chronic fatigue syndrome, asthma, and allergies.
Additionally, high dose Vitamin C has been found to reduce symptoms associated with cancer, positively impact glucose levels in type 2 diabetics, and may even have benefits in pneumonia, sepsis, and hepatitis. For those looking for a natural way to address a variety of ailments, these two treatments offer much promise.
In this article we will explore the latest research on The Myers Cocktail and High Dose Vitamin C so that you can make an informed decision about your health care options. We’ll look at what each treatment is intended to do and how their effects are being studied in clinical settings. We’ll also discuss potential side-effects and any precautions that should be taken when considering either treatment option.
Finally we’ll take a look at some common questions about both treatments. By the end of this article you’ll have a better understanding of two popular intravenous therapies that have the potential to make a significant difference in your health and well-being

Myers Cocktail
The “Myers Cocktail” is a popular intravenous nutrient infusion therapy that consists of a mixture of vitamins, minerals and other compounds. Several studies have been published showing the benefits of the Myers Cocktail for improving various medical conditions.
Fibromyalgia
A 2006 study found that after one to three treatments of Myers Cocktail, patients with fibromyalgia experienced a marked improvement in their symptoms. Specifically, the study noted a decrease in pain and fatigue, as well as a decrease in feelings of depression associated with the condition. Moreover, the infusion therapy was reported to significantly reduce levels of tenderness at acupuncture points and other areas associated with fibromyalgia. Additionally, participants also reported an increase in energy levels following treatment.
Further research conducted by the same authors revealed further positive results from Myers Cocktail infusions. A survey of 139 registered nurses who had received at least one infusion reported improved moods, increased energy, enhanced sleep quality and better overall wellbeing after treatment. In terms of pain reduction specifically, the survey indicated that more than two thirds of participants felt significant relief after just one session. Furthermore, the study noted that there were no adverse effects recorded during or after any treatments administered.
Overall, this body of research indicates that Myers Cocktail can be an effective form of treatment for individuals suffering from fibromyalgia due to its ability to reduce pain and fatigue while also improving mood and energy levels. Further studies are needed to conclusively understand the full extent of this type of infusion therapy’s efficacy in treating fibromyalgia-related symptoms. In 2015 I did a case study using the Myers Cocktail for a patient with Fibromyalgia. Check out the results by clicking HERE.
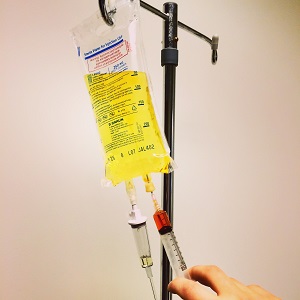
Chronic Fatigue
A 2008 study investigated the effects of the Myers Cocktail on patients with chronic fatigue syndrome (CFS). This was a double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of six months duration involving 24 participants. During the trial period, all participants were given either the Myers Cocktail or a placebo intravenously twice per week.
After six months, there was a marked improvement in energy levels and decrease in fatigue among participants who had received the Myers Cocktail compared to those who had been given a placebo. Specifically, individuals treated with the Myers Cocktail reported an average increase in energy levels of 41% and a reduction in fatigue by an average of 45%. In contrast, there was no significant change in energy levels or fatigue among those receiving the placebo.
The researchers also noted other positive effects of treatment including improved sleep quality and better mental clarity. Furthermore, they found that participants treated with the Myers Cocktail experienced less pain and an overall improvement in quality of life. These improvements were maintained over time, with no adverse effects reported during or after treatment.
Overall, this study demonstrates that the use of the Myers Cocktail may be beneficial for treating CFS as it appears to reduce fatigue levels as well as improve energy levels, sleep quality, mental clarity, pain and overall quality of life for those affected by CFS. Further research is needed to determine whether this is an effective long-term treatment option for CFS sufferers.
Allergies and Asthma
The 2015 systematic review investigated the use of intravenous vitamin therapies as an adjuvant therapy for allergies and asthma. The researchers analyzed the efficacy of popular infusions, such as the Myers Cocktail, in treating these conditions. Overall, their findings indicated that these therapies may be beneficial in reducing allergic reactions and improving symptoms of asthma. Specifically, their studies demonstrated a decrease in skin prick test reactivity against common allergens, such as dust mites and pollen, among patients who had received IV vitamin treatments. Additionally, some patients reported a reduction in airway resistance after treatment. Moreover, vitamin C was found to have anti-inflammatory properties that could help in easing symptoms associated with bronchial asthma. Finally, the review found that certain nutrients present in IV vitamins are important for the maintenance of a healthy respiratory system.
Overall, the studies indicated that there is evidence to suggest that intravenous vitamin therapies can be utilized as an adjuvant therapy for allergies and asthma when used alongside conventional medications. This is because they provide a multifaceted approach to tackling these conditions by alleviating both allergic responses and airway constriction caused by inflammation. As such, this type of therapy may offer additional benefits for those suffering from allergies or asthma compared to traditional medicaments alone.
Intravenous Vitamin C
Vitamin C is an essential vitamin with numerous health benefits, and high dose intravenous (IV) infusions of Vitamin C have been used to treat a variety of medical conditions.
Cancer
The 2017 study conducted by researchers at the University of Kentucky Markey Cancer Center revealed that high-dose vitamin C IV infusion could be an effective form of treatment for cancer patients. The study included 20 participants who were randomly assigned to receive either a placebo or infusions of high-dose vitamin C. After 8 weeks, the researchers evaluated the participants’ symptoms and found that those who received the infusions experienced notable reductions in pain, fatigue, anxiety, and depression.
Not only did the participants experience a significant improvement in physical and mental health, but their overall quality of life was also enhanced. Furthermore, blood work showed that the patients’ levels of biomarkers associated with tumor activity had decreased significantly. This suggests that high-dose vitamin C IV infusion may actually help reduce tumor growth as well. While these findings are promising, more research is needed to determine whether this treatment is truly effective for cancer patients in the long term.

Diabetes
A study, conducted in 2018, found that high-dose vitamin C IV infusion can have positive effects on diabetes symptoms and glucose levels in individuals with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Using a randomized controlled trial, the research team found that after 30 days of treatment with vitamin C infusions, patients showed significant improvements in their HbA1c levels and fasting blood glucose levels, compared to a control group receiving no treatment.
Additionally, those receiving the vitamin C infusions reported lower rates of fatigue and improved quality of life. The researchers also noted that the therapy was well-tolerated with no serious adverse effects reported.
Moreover, the study revealed that regular treatments with high-dose vitamin C may be beneficial for managing diabetes symptoms over time. This is due to its antioxidant properties which can help reduce oxidative stress and inflammation caused by elevated glucose levels in T2DM patients.
Furthermore, it has been suggested that this type of therapy could be combined with conventional drug treatments to better manage the condition. Ultimately, these findings indicate potential therapeutic benefits of high-dose vitamin C infusions for those living with type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Vitamin C IV in various conditions
A 2019 systematic review conducted by researchers evaluated the effectiveness of high-dose vitamin C IV infusions in treating various medical conditions, such as cancer, pneumonia, sepsis and hepatitis. The study included 21 trials with a total of 590 participants. The researchers concluded that evidence was present to support the use of vitamin C IV infusions as an adjunctive therapy for some conditions.
For instance, one trial found that intravenous high-dose vitamin C improved overall survival rate in patients with advanced pancreatic cancer compared with conventional chemotherapy alone. Another study showed that vitamin C IV infusion helped reduce mortality rate among sepsis patients. Regarding pneumonia, high-dose vitamin C infusions were also found to improve quality of life and reduce hospital stay compared to placebo. When it comes to hepatitis, one trial reported improvement in liver function tests following administration of vitamin C IV infusion.
Overall, the findings from this systematic review suggest that there is potential for high-dose intravenous vitamin C being used as an adjunct therapy for certain medical conditions such as cancer, pneumonia, sepsis and hepatitis.
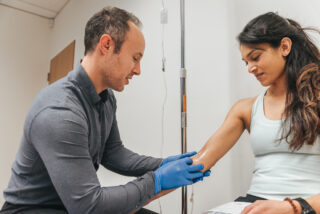
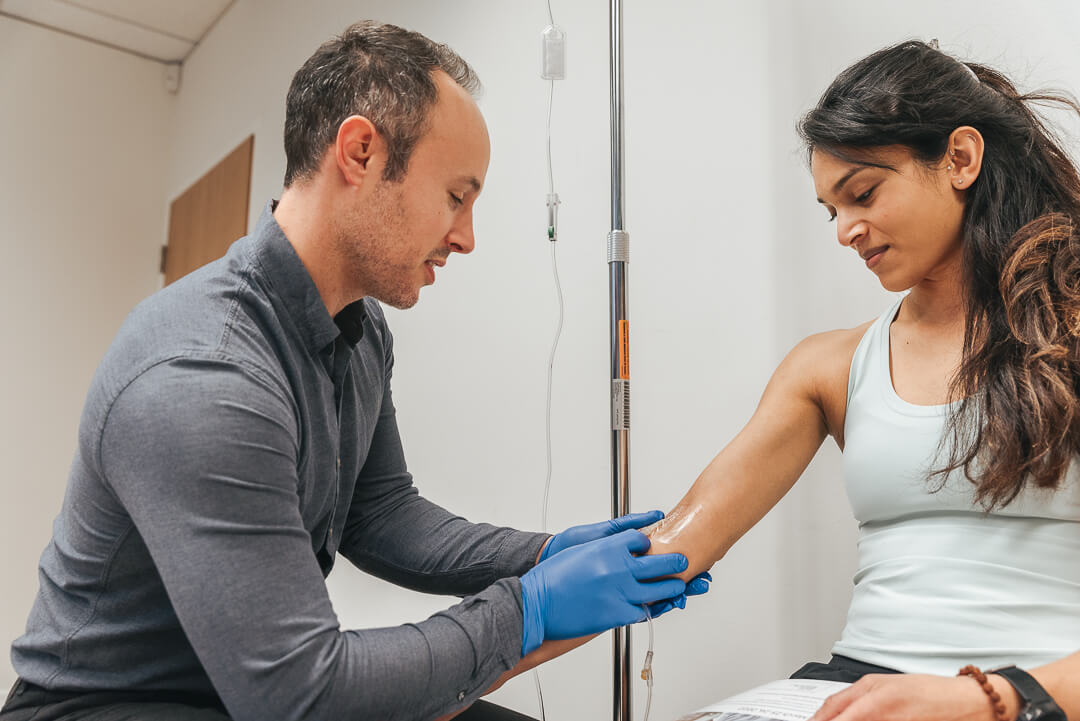
Conclusion
Myers Cocktail and High Dose Vitamin C IV therapy have both been shown to be beneficial in various different health conditions. While Myers Cocktail is particularly helpful for Fibromyalgia, Chronic Fatigue Syndrome, Allergies and Asthma, high dose Vitamin C has been linked to improved outcomes in cancer, diabetes, pneumonia, sepsis and hepatitis.
The research around the effects of these therapies is still ongoing and it is vital that further studies are conducted to better understand their potential for treating a variety of illnesses. At the same time however, more clinical trials should also be undertaken to ascertain their effectiveness when compared to other treatments currently available.
Although there are many potential benefits associated with both the Myers Cocktail and High Dose Vitamin C IV therapies, it is important that individuals consult with their IV therapy specialist before pursuing either treatment. This will ensure that they receive the most appropriate care for their individual needs and circumstances. For more information on IV therapies offered at my clinic Click Here
References
- The 2006 study on the Myers Cocktail for fibromyalgia can be found in Bloom, 2006.
- The 2008 study on the Myers Cocktail for chronic fatigue syndrome (CFS) can be found in Forsyth, 2008.
- The 2015 systematic review of intravenous vitamin therapies for asthma and allergies can be found in Brown et al., 2015.
- The 2017 study on high dose vitamin C IV infusion and cancer can be found in Kanematsu et al., 2017
- The 2018 study on high dose vitamin C IV infusion and type 2 diabetes Mellitus (T2DM) can be found in Maeda et al., 2018
- -The 2019 systematic review of high dose Vitamin C IV infusions for various medical conditions can be found in Wang et al., 2019(https://www.ncbi.nlm
Intro to Naturopathic Pediatrics
Naturopathic Pediatrics is an alternative health system that focuses on the whole person. It combines modern scientific knowledge and traditional natural medicine techniques to help children achieve optimal health. Let’s explore some of the benefits of Naturopathic Pediatrics so you can make an informed decision on behalf of your child’s health.
Holistic Approach to Wellness
Naturopathic Pediatrics takes a holistic approach to wellness, which means that it considers all aspects of a person’s life. Physical health, mental health and emotional health are all taken into account when providing treatment. This type of approach is especially beneficial for children since it focuses on treating the cause of illness in addition to its symptoms. It also allows practitioners to work closely with parents and their children in order to create a tailored plan that will best address the specific needs of each individual patient.
Safe and Effective Treatments
Naturopathy offers safe and effective treatments for many common childhood illnesses such as allergies, asthma, ear infections, colds and flus. Instead of relying on pharmaceutical drugs or invasive therapies, Naturopathy focuses on identifying underlying causes and using natural remedies to improve overall health without harsh side effects. Natural treatments may include dietary changes, herbal remedies, homeopathy, acupuncture, massage therapy or lifestyle modifications like increased physical activity or improved sleep hygiene.
Additionally, Naturopathy can help support the long-term health of your child by strengthening their immune system and helping them develop healthy habits that will last into adulthood.
Naturopaths also offer a wide range of functional testing aimed at optimizing health and investigating the root cause of disease. Some of these tests include: food sensitivity testing, organic acids testing, hormone profiles and nutritional deficiencies. Check out some of the tests we offer by clicking HERE
Research on Naturopathic care for children
Naturopathic care for children is becoming increasingly popular among parents concerned about the health and wellbeing of their kids. Research from the National Institutes of Health (NIH) has demonstrated that naturopathic care can help reduce common childhood illnesses like colds, flu and digestive issues 1.
Additionally, studies from the American Medical Association (AMA) have shown that naturopathic treatments offer powerful healing benefits when used to treat chronic ailments such as asthma, diabetes or ADD/ADHD 2.
Other research indicates that naturopathy can also be a great way to avoid the use of unnecessary medications in children, making it a viable option for parents who are looking for an alternative form of healthcare for their young ones 3.
Personalized Care
The personalized care provided by naturopaths is invaluable when it comes to providing quality healthcare for your child. Your naturopath will take time to get to know both you and your child in order to determine the best course of action for their particular situation. They will provide guidance and support throughout the entire process in order to ensure that your child’s needs are being met at every step along the way. Additionally, naturopaths often provide resources such as handouts or websites that can be utilized at home in order to further empower both parents and children throughout their journey towards optimal health.
Conclusion
The benefits of Naturopathic Pediatrics are numerous: from its holistic approach to wellness; its safe and effective treatments; its personalized care; there is no doubt why this form of alternative medicine is gaining popularity among parents seeking better health care options for their children. If you’re looking for an alternative approach focused on restoring balance within your child’s body then consider giving Naturopathic Pediatrics a try today!
Ready to book an appointment? Click HERE
Sources
1 https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4789024/
2 https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamapediatrics/fullarticle/2550272
3 https://www.natureandforesttherapy.org/naturopathy-for-children